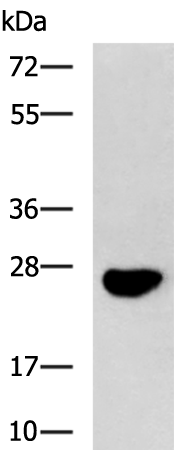
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C1QG; C1Q-C |
| WB Predicted band size | 26 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human C1QC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与C1QC抗体相关的研究文献摘要概览:
1. **"Autoantibodies against C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus"**
*作者:Trendelenburg M, et al.*
摘要:该研究探讨了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者中抗C1q自身抗体的病理意义,发现其与肾脏损伤(狼疮性肾炎)和疾病活动度显著相关,提示其可作为SLE的生物标志物。
2. **"C1q and tumor-associated macrophages: A novel prognostic marker in cancer"**
*作者:Zhang Y, et al.*
摘要:研究揭示了C1QC在肿瘤微环境中高表达于M2型巨噬细胞,其水平与免疫抑制性微环境形成相关,可作为癌症患者预后评估的潜在靶点。
3. **"Structural insights into the function of C1q in the complement system"**
*作者:Ghai R, et al.*
摘要:通过晶体学分析C1q复合物(含C1QC亚基)的结构,阐明其在补体经典激活途径中的关键作用,为开发靶向C1QC的抗体药物提供理论依据。
4. **"Genetic variants of C1QC and their association with inflammatory diseases"**
*作者:Bohlson SS, et al.*
摘要:研究发现C1QC基因多态性与类风湿性关节炎等慢性炎症性疾病易感性相关,提示C1QC抗体可能参与调控补体介导的炎症反应。
*注:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索确认。*
C1q antibodies target a key component of the complement system, specifically the C1q protein within the C1 complex. C1q, composed of six collagen-like stalks and globular heads, initiates the classical complement pathway by binding to antigen-antibody complexes or pathogen surfaces. This interaction triggers a proteolytic cascade, leading to pathogen opsonization, inflammation, and immune clearance. C1q also plays roles in apoptotic cell removal and immune tolerance.
C1QC, the gene encoding the C-chain of C1q, is critical for maintaining structural integrity and functional activity of the C1q molecule. Antibodies against C1q (anti-C1q) are clinically significant, particularly in autoimmune diseases like lupus nephritis and hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome (HUVS). In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), anti-C1q antibodies correlate with renal involvement and disease severity, often targeting the collagen-like region of C1q, which may disrupt immune complex clearance.
Research applications of C1q antibodies include studying complement activation mechanisms, autoimmune pathogenesis, and tissue injury models. They are used in techniques like ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to quantify C1q levels or map its distribution in tissues. Recent studies also explore their role in neurodegenerative diseases, where aberrant complement activity contributes to neuroinflammation. Understanding C1q biology and its antibodies offers insights into therapeutic strategies for modulating complement-driven pathologies.
×