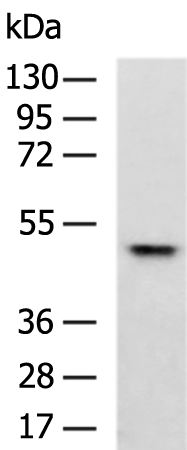
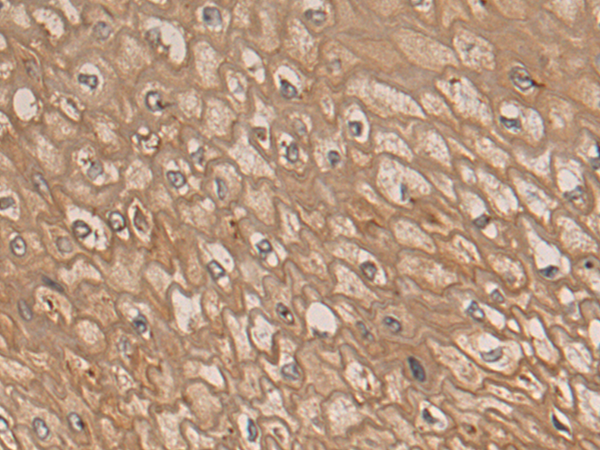
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CD14 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD14抗体的3篇参考文献,按研究领域和发表时间整理:
1. **文献名称**: *CD14. a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and LPS binding protein*
**作者**: Wright SD, Ramos RA, Tobias PS, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次阐明CD14作为脂多糖(LPS)与LPS结合蛋白复合物的受体功能,揭示其在先天免疫中识别革兰氏阴性菌感染的关键作用,并推动后续针对脓毒症治疗的抗体开发。
2. **文献名称**: *CD14-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells: Relevance to the immune system*
**作者**: Devitt A, Moffatt OD, Raykundalia C, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现CD14通过识别凋亡细胞表面的磷脂酰丝氨酸,介导巨噬细胞对凋亡细胞的吞噬作用,表明CD14抗体可能调控炎症性疾病中免疫耐受的失衡。
3. **文献名称**: *Soluble CD14 subtype (sCD14-ST) as a biomarker for sepsis diagnosis: A meta-analysis*
**作者**: Zhang X, Liu D, Liu YN.
**摘要**: 通过荟萃分析验证可溶性CD14亚型(sCD14-ST)在脓毒症早期诊断中的高敏感性和特异性,强调针对该亚型的单克隆抗体在临床诊断试剂中的应用潜力。
CD14 is a glycoprotein surface antigen primarily expressed on monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, serving as a co-receptor for detecting bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in innate immunity. Functionally, it binds to LPS-binding protein (LBP) complexes, facilitating the recognition of LPS and other pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). This interaction triggers intracellular signaling through Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), initiating pro-inflammatory responses critical for combating infections. CD14 exists in two forms: membrane-bound (mCD14) anchored via glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) and soluble (sCD14) released into circulation, both implicated in modulating immune activation and sepsis pathology.
CD14 antibodies, developed as monoclonal or polyclonal reagents, are essential tools for identifying monocyte/macrophage populations in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional studies. They target specific epitopes on CD14. enabling researchers to study its role in infectious diseases, chronic inflammation, and immune regulation. Clinically, CD14 expression levels correlate with disease states like septic shock, atherosclerosis, and autoimmune disorders, making these antibodies valuable for diagnostic and therapeutic research. Additionally, CD14-targeting therapies are explored to mitigate excessive inflammation in sepsis or enhance pathogen clearance. The antibody's utility extends to investigating crosstalk between innate and adaptive immunity, as CD14⁺ cells influence T-cell responses and tissue repair mechanisms.
×