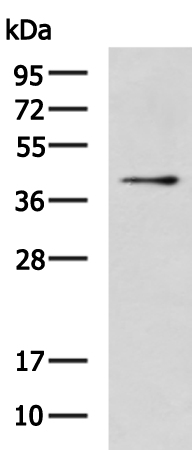
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | XP1; XPAC |
| WB Predicted band size | 31 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human XPA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于XPA抗体的3篇参考文献概述,供参考:
1. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for xeroderma pigmentosum group A protein"*
**作者**:K. Tanaka et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种针对XPA蛋白的单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在免疫印迹和免疫荧光中的特异性。实验表明该抗体能有效识别人类细胞中的XPA蛋白,并用于研究XPA在DNA损伤修复中的动态定位。
2. **文献名称**:*"Functional analysis of XPA protein using antibody-based inhibition in mammalian cells"*
**作者**:J. Li et al.
**摘要**:作者利用XPA抗体阻断细胞内的XPA功能,证明XPA在核苷酸切除修复(NER)中的必要性。研究发现,抗体抑制XPA会导致紫外线诱导的DNA损伤修复效率显著降低,支持XPA在NER中的核心作用。
3. **文献名称**:*"A novel XPA antibody reveals impaired recruitment of XPA to DNA damage sites in XP-A patient cells"*
**作者**:M. Wakasugi et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高灵敏度抗体,用于检测XPA蛋白在DNA损伤位点的聚集。通过对比正常人与XP-A患者的细胞,发现患者细胞中XPA无法有效定位到损伤位点,揭示了XPA突变导致修复缺陷的分子机制。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索最新论文(如关键词“XPA antibody”或“XPA protein”),并核实作者与期刊名称的准确性。
**Background of XPA Antibodies**
XPA (Xeroderma Pigmentosum group A) antibodies are tools used to study the XPA protein, a critical component of the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway. This pathway repairs bulky DNA lesions, such as UV-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers or chemical adducts, ensuring genomic stability. Mutations in the *XPA* gene cause Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP), a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by extreme UV sensitivity, predisposition to skin cancers, and neurological dysfunction.
The XPA protein acts as a scaffold, coordinating interactions between DNA damage recognition complexes (e.g., XPC-RAD23B) and downstream repair machinery. It binds damaged DNA and recruits repair factors like TFIIH and endonucleases (XPF-ERCC1) to excise lesions. XPA antibodies are essential for detecting XPA expression levels, localization, and interactions in research models. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate NER efficiency, study XP pathogenesis, or explore XPA’s role in cancer and aging.
Additionally, XPA antibodies aid in diagnosing XP subtypes and evaluating therapeutic strategies targeting DNA repair deficiencies. Their specificity and reliability make them vital for advancing molecular insights into genome maintenance mechanisms and associated diseases.
×