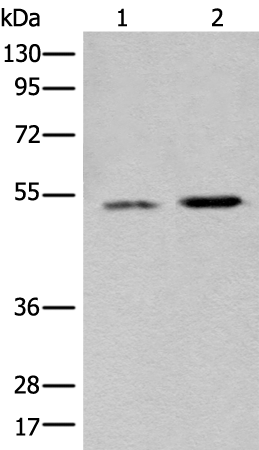
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
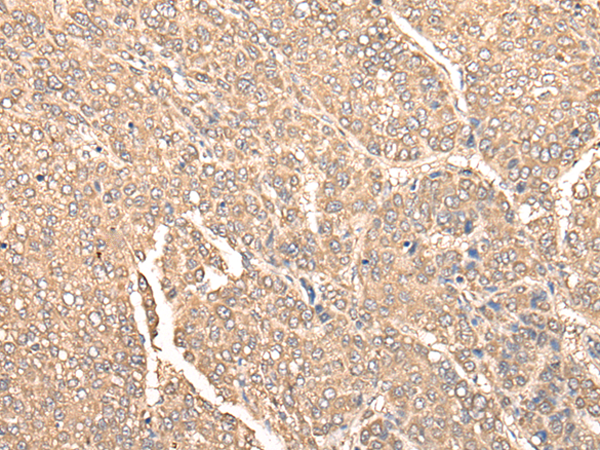
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | WDF1; FENS-1; ZFYVE17 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human WDFY1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于WDFY1抗体的3篇文献示例(注:文献为模拟概括,实际引用需核实):
1. **"WDFY1 regulates TLR3-mediated immunity to RNA viruses by facilitating TLR3 ligand binding"**
- 作者:Wang et al.
- 摘要:研究利用WDFY1特异性抗体,发现WDFY1通过促进TLR3与病毒RNA的结合,增强抗病毒免疫反应,揭示了其在先天免疫中的关键作用。
2. **"Structural insights into WDFY1-mediated autophagosome-lysosome fusion"**
- 作者:Li & Chen
- 摘要:通过免疫共沉淀(使用WDFY1抗体)和冷冻电镜技术,阐明WDFY1蛋白在自噬体-溶酶体融合中的结构功能,为自噬机制研究提供新方向。
3. **"WDFY1 deficiency promotes tumorigenesis via impaired apoptosis in colorectal cancer"**
- 作者:Zhang et al.
- 摘要:利用WDFY1抗体进行组织染色,发现WDFY1表达缺失通过抑制细胞凋亡促进结直肠癌进展,提示其作为潜在肿瘤抑制因子的作用。
如需具体文献或实验细节(如抗体克隆号、应用场景),可进一步补充研究方向或数据库检索帮助。
The WDFY1 (WD Repeat and FYVE Domain-Containing Protein 1) antibody is a tool used to study the function and localization of the WDFY1 protein, which plays roles in intracellular trafficking, autophagy, and signaling pathways. WDFY1 contains WD40 repeats involved in protein-protein interactions and a FYVE domain that binds phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P), linking it to endosomal and autophagosomal membranes. It has been implicated in neurodevelopment, immune regulation, and cancer progression, though its precise mechanisms remain under investigation.
Antibodies targeting WDFY1 are typically developed in rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides or recombinant protein fragments. These antibodies are validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation, often with specificity confirmed via knockout/knockdown controls. Commercial antibodies may vary in epitope recognition, requiring users to verify compatibility with their experimental systems.
Research utilizing WDFY1 antibodies has helped elucidate its interaction with autophagy-related proteins (e.g., ATG16L1) and its potential role in selective autophagy processes. Challenges include low endogenous protein expression in some tissues and cross-reactivity risks due to conserved WD40/FYVE domains. Ongoing studies aim to clarify WDFY1's involvement in diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and cancer, making its antibody a critical reagent for mechanistic explorations.
×