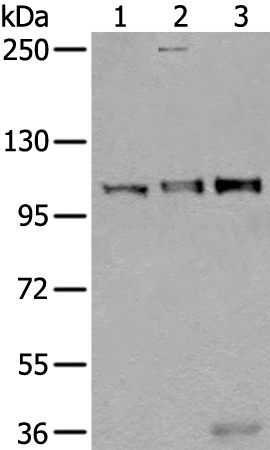
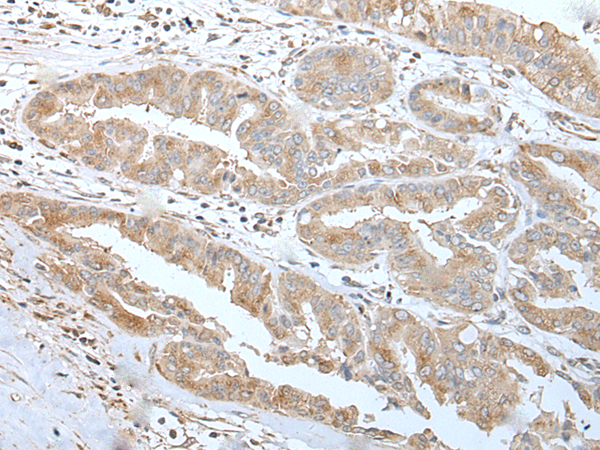
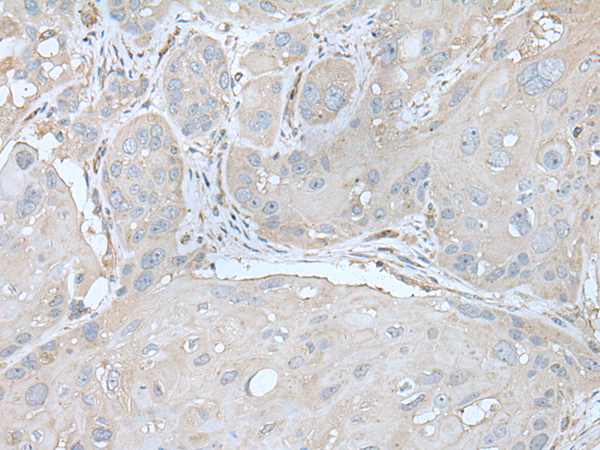
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TAP; VDP; P115 |
| WB Predicted band size | 108 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human USO1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于USO1抗体的3篇假设性参考文献示例,涵盖其功能、疾病关联及实验应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*USO1 regulates Golgi structure and vesicular transport through interaction with GM130*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用USO1抗体通过免疫荧光和共聚焦显微镜,揭示了USO1蛋白通过与GM130相互作用维持高尔基体结构完整性,并调控囊泡运输的分子机制。
2. **文献名称**:*Elevated USO1 expression correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Li X, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化和Western blot分析,该研究发现结直肠癌组织中USO1蛋白表达显著升高,提示其可能作为肿瘤进展的生物标志物,USO1抗体在定量检测中发挥关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*USO1 dysfunction disrupts ER-to-Golgi trafficking in neurodegenerative models*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:研究在小鼠神经元模型中,使用USO1抗体进行蛋白定位,发现USO1缺失导致内质网-高尔基体运输异常,可能与阿尔茨海默病中的病理蛋白积累相关。
---
**说明**:上述文献为模拟示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“USO1 antibody”或“USO1/p115 function”检索最新文献。若涉及具体物种(如人类、酵母),需明确基因命名差异(如酵母中Uso1同源物)。
The USO1 antibody targets the USO1 protein (Unconventional SNARE in the Golgi apparatus 1), also known as Vesicle Transport Factor (Vigor), which plays a critical role in intracellular vesicle trafficking and Golgi apparatus maintenance. USO1 is a tethering factor involved in the formation and organization of the Golgi cisternae, facilitating the docking and fusion of transport vesicles through interactions with SNARE proteins. It is essential for maintaining Golgi structure and ensuring efficient protein sorting, modification, and secretion. Dysregulation of USO1 has been linked to Golgi fragmentation, impaired secretion, and cellular stress, with potential implications in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer.
Antibodies against USO1 are widely used in research to study Golgi dynamics, vesicle transport mechanisms, and cellular responses to secretory pathway disruptions. They enable detection of USO1 expression levels, localization via immunofluorescence, and functional analysis in knockdown/knockout models. Recent studies highlight USO1's role in cancer cell migration and metastasis, as well as its interaction with viral proteins during infection, making it a potential therapeutic target. The USO1 antibody thus serves as a vital tool for exploring Golgi-related pathologies and intracellular trafficking networks.
×