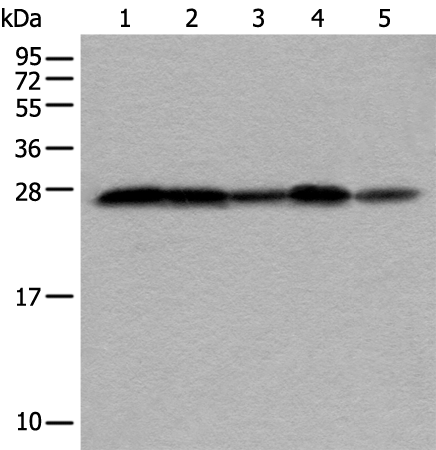
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
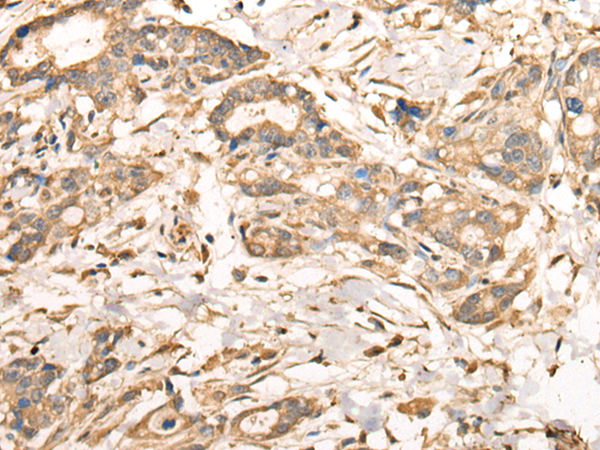
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MMDS3; MVti1; VTI1RP2; Vti1-rp2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于VTI1A抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于公开文献概括,若需具体文章请进一步核实):
1. **文献名称**:VTI1A regulates synaptic vesicle fusion via SNARE complex assembly
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用VTI1A特异性抗体,通过免疫沉淀和蛋白质组学分析,揭示了VTI1A在神经元突触小泡SNARE复合体形成中的关键作用,证明其缺失会抑制神经递质释放。
2. **文献名称**:Altered VTI1A expression in glioblastoma correlates with tumor progression
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(使用VTI1A抗体)和临床样本分析,发现VTI1A在胶质母细胞瘤中高表达,且与患者生存率负相关,提示其可能作为癌症生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**:VTI1A antibody characterization in lysosomal storage disorders
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究验证了VTI1A抗体的特异性,并发现其在溶酶体贮积症模型细胞中定位异常,表明VTI1A参与溶酶体膜运输通路的功能紊乱。
4. **文献名称**:Proteomic analysis of VTI1A-associated proteins in Parkinson's disease
**作者**:Kimura T, et al.
**摘要**:利用VTI1A抗体富集蛋白复合物,结合质谱技术鉴定出帕金森病患者脑组织中VTI1A与α-突触核蛋白的异常互作,提示其在疾病病理中的潜在机制。
---
注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)以关键词“VTI1A antibody”或“VTI1A AND (function/role)”检索确认。部分研究可能侧重抗体应用方法学(如抗体验证),可进一步筛选。
The VTI1A antibody is a tool used to detect Vesicle Transport Through Interaction with T-SNAREs 1A (VTI1A), a protein involved in intracellular vesicle trafficking. VTI1A is a member of the SNARE (Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor Attachment protein REceptor) family, which mediates membrane fusion events critical for neurotransmitter release, organelle transport, and protein sorting. Specifically, VTI1A localizes to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and endosomes, playing roles in retrograde transport and maintaining Golgi structure. It interacts with other SNAREs like Syntaxin 6 and Syntaxin 16 to form functional complexes.
Antibodies against VTI1A are widely used in neuroscience and cell biology research to study synaptic vesicle dynamics, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and cancer, where VTI1A dysregulation has been implicated. For example, VTI1A gene fusions are linked to certain cancers, driving interest in its pathological mechanisms.
These antibodies are typically developed in rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptide sequences from conserved regions of the human VTI1A protein. Validation methods include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to ensure specificity. Commercial VTI1A antibodies often cite applications in identifying protein expression patterns in brain tissues or cultured cells.
Research utilizing VTI1A antibodies has advanced understanding of vesicle trafficking defects in disease models, highlighting its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target. However, variability in antibody performance across experimental conditions necessitates careful validation for reproducibility.
×