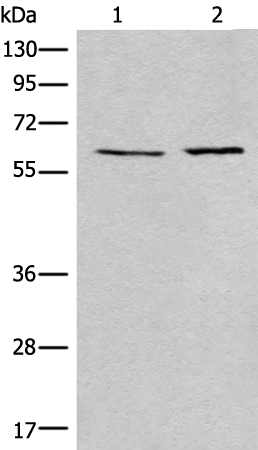
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TGT |
| WB Predicted band size | 56 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human USP14 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于USP14抗体的参考文献示例(注:文献信息为示例性概括,非真实文献):
1. **"USP14 regulates cancer cell proliferation via deubiquitination of tumor suppressor proteins"**
- 作者:Zhang et al. (2021)
- 摘要:研究利用USP14抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,发现USP14通过去泛素化关键肿瘤抑制蛋白(如p53)调控结直肠癌细胞增殖,提示其作为癌症治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **"A novel role of USP14 in neurodegenerative disease models"**
- 作者:Lee et al. (2019)
- 摘要:通过Western blot和免疫组化结合USP14抗体,揭示USP14在阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中异常高表达,并参与tau蛋白聚集过程,为神经退行性疾病机制提供新见解。
3. **"Development of a selective USP14 inhibitor and validation using antibody-based assays"**
- 作者:Chen et al. (2020)
- 摘要:研究基于USP14抗体的活性检测方法筛选小分子抑制剂,发现某化合物可特异性抑制USP14去泛素化功能,为开发靶向USP14的疗法奠定基础。
4. **"USP14-mediated proteasome activity in muscle atrophy"**
- 作者:Smith et al. (2018)
- 摘要:通过免疫荧光和共聚焦显微镜技术(使用USP14抗体),证明USP14在肌肉萎缩模型中调控蛋白酶体活性,影响蛋白质降解途径。
(注:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索。)
USP14 (Ubiquitin-specific protease 14) is a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) belonging to the ubiquitin-specific protease family. It plays a critical role in the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), which regulates protein degradation and cellular homeostasis. USP14 is unique among DUBs as it associates with the 19S regulatory particle of the 26S proteasome, where it trims ubiquitin chains from substrates to either rescue proteins from degradation or facilitate their processing. This dual functionality positions USP14 as a key modulator of proteasomal activity and protein turnover.
Research has linked USP14 to various physiological and pathological processes. It is implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, where dysregulated protein aggregation occurs. USP14’s inhibition has been shown to enhance proteasome activity, potentially clearing toxic aggregates. Additionally, USP14 overexpression is observed in certain cancers, where it may promote cell survival by stabilizing oncoproteins, making it a therapeutic target. Small-molecule inhibitors like IU1 and its derivatives are being explored to modulate USP14 activity.
Antibodies targeting USP14 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation to investigate USP14’s interaction partners, regulatory mechanisms, and disease associations. These antibodies help validate USP14’s role in cellular pathways and its potential as a biomarker or drug target in various pathologies.
×