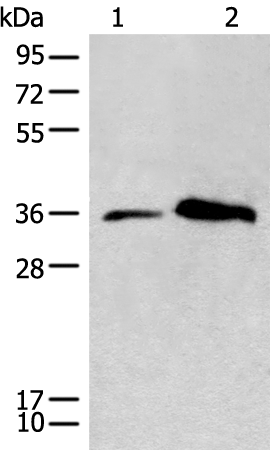
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
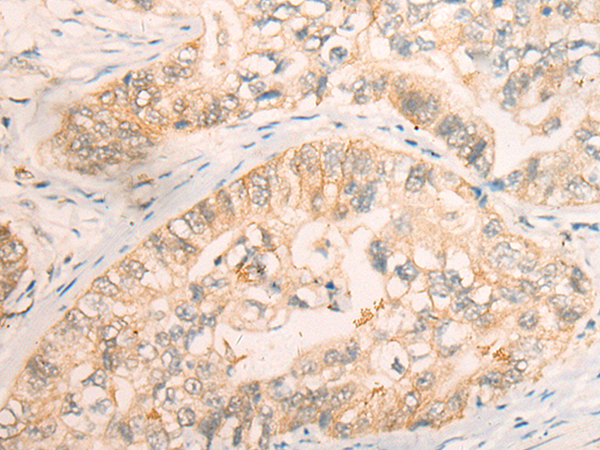
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B70; B7-2; B7.2; LAB72; CD28LG2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CD86 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD86抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要:
1. **"The B7-CD28 superfamily"**
*作者:Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ*
摘要:综述了B7家族(包括CD86/CD80)与CD28/CTLA-4受体的相互作用机制,强调CD86抗体通过阻断共刺激信号抑制T细胞活化,在自身免疫病和移植排斥中的潜在治疗价值。
2. **"CD86 and CD80 differentially modulate the suppressive function of human regulatory T cells"**
*作者:Greenfield EA, Nguyen KA, Kuchroo VK*
摘要:研究显示,抗CD86抗体选择性抑制效应T细胞增殖,但增强调节性T细胞(Treg)的免疫抑制功能,为靶向CD86治疗炎症性疾病提供理论依据。
3. **"Differential effects of anti-CD80 and anti-CD86 antibodies on murine T cell activation"**
*作者:Hathcock KS, Laszlo G, Dickler HB*
摘要:通过小鼠模型证明,CD86抗体在免疫反应早期阶段阻断CD28结合更有效,而CD80抗体对CTLA-4信号调控更显著,提示两者在时序和功能上的互补性。
4. **"Anti-CD86 monoclonal antibody inhibits T cell cytokine production and migration in psoriasis models"**
*作者:Suvas S, Singh V, Sahdev S*
摘要:在银屑病小鼠模型中,抗CD86抗体通过抑制IL-17/IFN-γ分泌和T细胞皮肤浸润,显著减轻病理症状,验证其治疗Th17介导疾病的潜力。
CD86. also known as B7-2. is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the B7 family of immune checkpoint molecules. It is primarily expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and activated B cells. CD86 interacts with CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors on T cells, playing a pivotal role in modulating T-cell activation and immune response regulation. During antigen presentation, CD86 binds to CD28 on naïve T cells, delivering a co-stimulatory signal required for full T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production alongside T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling. Conversely, its interaction with CTLA-4 (expressed on activated T cells) transmits inhibitory signals to dampen immune responses, maintaining peripheral tolerance and preventing autoimmunity.
CD86 antibodies are critical tools in research and therapeutic development. In experimental settings, they are used to block or stimulate CD86-mediated pathways to study immune activation mechanisms, tolerance, and diseases like cancer, autoimmune disorders, or transplant rejection. Therapeutically, CD86-targeting agents (e.g., fusion proteins like abatacept) are explored to modulate immune activity—either suppressing hyperactive responses in autoimmune conditions or enhancing anti-tumor immunity by disrupting checkpoint inhibition. Due to its transient expression kinetics (upregulated earlier than CD80/B7-1 during APC activation), CD86 is considered a key early regulator of adaptive immunity, making it a strategic target for precision immunotherapy approaches.
×