| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
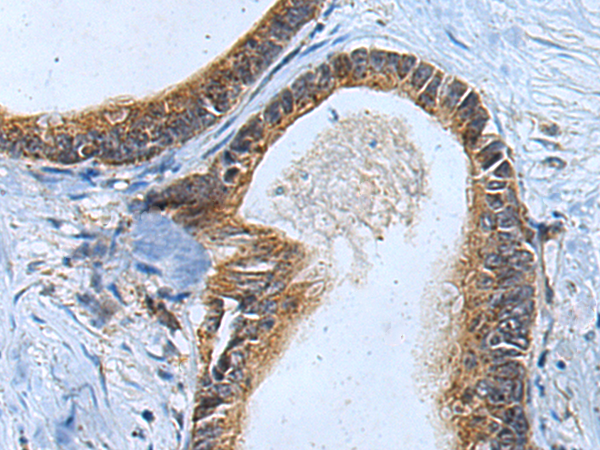
| IHC | 1/150-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BL11; HB15 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CD83 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD83抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*CD83: A Regulator of Immune Checkpoints in Dendritic Cell Function*
**作者**:Lechmann M, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了CD83在树突状细胞(DC)成熟中的关键作用,发现CD83抗体可通过阻断其信号通路抑制DC的抗原呈递能力,从而调节T细胞激活,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD83 for the Treatment of Allograft Rejection*
**作者**:Fujimoto Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗CD83单克隆抗体在小鼠移植模型中抑制宿主DC功能,显著延长移植物存活时间,表明CD83抗体在预防器官移植排斥反应中的潜在应用价值。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD83 Antibody Enhances Antitumor Immunity by Modulating Tumor Microenvironment*
**作者**:Smith C, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了抗CD83抗体通过重塑肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制性细胞群(如调节性T细胞),增强CAR-T细胞疗法的抗肿瘤效果,为癌症免疫联合治疗提供新策略。
4. **文献名称**:*CD83 Shedding and Soluble Form in Immune Regulation*
**作者**:Bock F, et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了抗CD83抗体通过抑制膜型CD83的酶切脱落,维持其膜表面稳定性,进而增强DC与T细胞间的相互作用,影响炎症反应的动态平衡。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对真实存在的论文信息。)
CD83 is a transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on the surface of mature dendritic cells (DCs), key regulators of adaptive immunity. First identified in the 1990s, CD83 plays a critical role in immune modulation, particularly in T-cell activation and immune tolerance. Its expression is tightly regulated during DC maturation, making it a reliable marker for distinguishing mature DCs from their immature counterparts. Structurally, CD83 consists of an extracellular Ig-like domain, a transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail. A soluble form (sCD83) is also generated through proteolytic cleavage or alternative splicing, which exhibits immunosuppressive properties.
CD83 antibodies are essential tools in immunological research and therapeutic development. They are widely used to study DC-T cell interactions, immune synapse formation, and mechanisms underlying autoimmune diseases, transplantation tolerance, and cancer immunotherapy. For instance, agonistic anti-CD83 antibodies have shown potential in enhancing DC-mediated immune responses, while blocking antibodies or sCD83 fusion proteins may suppress aberrant immune activation in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or graft-versus-host disease. Commercial CD83 antibodies (e.g., clone HB15e for flow cytometry, HI83a for functional studies) enable DC phenotyping in human and murine models. Ongoing research explores CD83-targeting strategies for modulating immune responses, balancing its dual roles in immune activation and tolerance induction.
×