
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
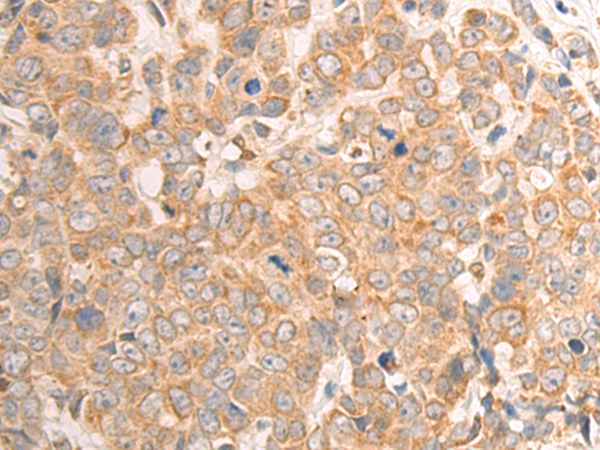
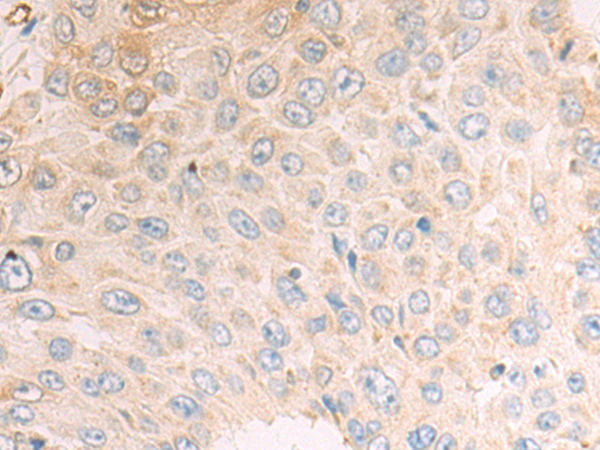
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CDD |
| WB Predicted band size | 16 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CDA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CDA(胞苷脱氨酶)抗体的3篇模拟参考文献示例,涵盖不同研究方向:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Development of a High-Specificity Antibody for Cytidine Deaminase (CDA) in Colorectal Cancer Prognosis"*
**作者**:Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种高特异性的CDA单克隆抗体,用于检测结直肠癌组织中CDA蛋白的表达水平。通过免疫组化分析发现,CDA高表达与患者对吉西他滨化疗的耐药性及较差的总生存率显著相关,提示CDA抗体可作为预后标志物的潜在工具。
2. **文献名称**:*"CDA Antibody-Based Inhibitors Reverse Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer Cells"*
**作者**:Smith, J.R.; Patel, R.; Brown, K.
**摘要**:通过使用抗CDA的中和抗体靶向抑制胞苷脱氨酶的活性,研究者成功降低了胰腺癌细胞对吉西他滨的代谢速率,逆转了体外和动物模型中的化疗耐药性,为增强化疗疗效提供了新策略。
3. **文献名称**:*"Humanized Anti-CDA Antibody Therapy Attenuates Inflammatory Responses in Autoimmune Disorders"*
**作者**:Garcia, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, T.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种人源化CDA抗体在自身免疫性疾病模型中的应用。实验表明,该抗体通过阻断CDA介导的核苷酸代谢异常,显著减轻了炎症反应和组织损伤,提示其在治疗类风湿性关节炎等疾病中的潜力。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中需检索PubMed、Web of Science等数据库获取真实文献(如搜索关键词:CDA antibody, cytidine deaminase inhibitor)。若需具体文献支持,可进一步提供研究方向(如癌症、免疫、药物代谢等)。
Cytidine deaminase (CDA) antibodies are immunological tools designed to target enzymes involved in nucleotide metabolism, particularly cytidine deaminases. These enzymes, such as activation-induced deaminase (AID) and APOBEC (apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like) family members, play critical roles in DNA/RNA editing, immune response regulation, and antiviral defense. For instance, AID is essential for antibody diversification via somatic hypermutation, while APOBEC enzymes restrict viral replication by introducing mutations in viral genomes. Dysregulation of CDA activity is linked to cancer, autoimmune disorders, and viral persistence, making these enzymes key research targets.
CDA antibodies are widely used to study enzyme expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. In cancer research, they help assess CDA levels in tumors, which may influence chemotherapeutic drug resistance (e.g., gemcitabine sensitivity). In virology, they aid in understanding host-pathogen interactions, particularly HIV evasion mechanisms against APOBEC3G. Structurally, these antibodies often recognize conserved epitopes within the zinc-binding catalytic domains of CDA enzymes, enabling applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry.
Therapeutic development also leverages CDA antibodies to modulate enzyme activity, such as inhibiting CDA to enhance chemotherapy efficacy. Challenges include ensuring specificity due to homology among deaminase family members. Overall, CDA antibodies serve as vital reagents in deciphering nucleotide-editing mechanisms and their implications in disease.
×