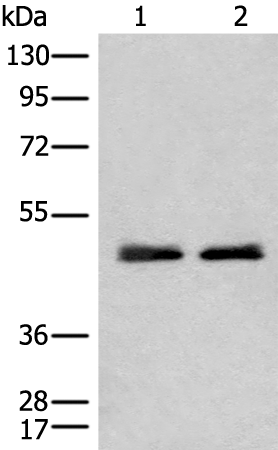
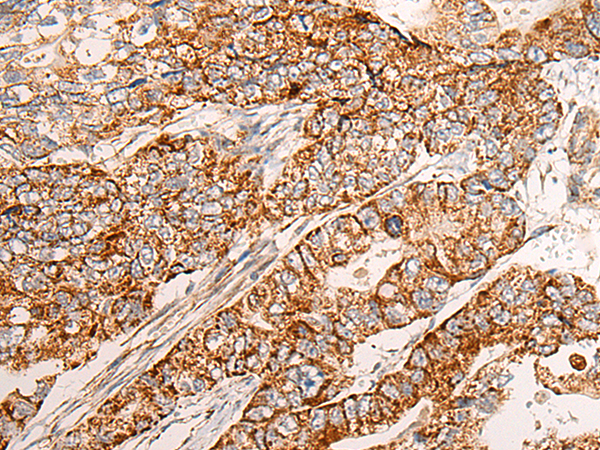
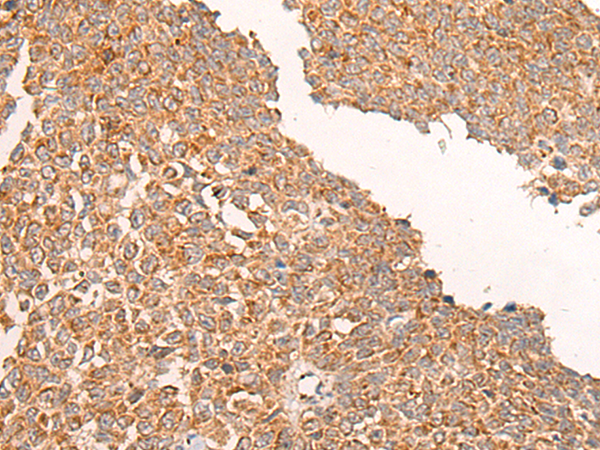
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CHI3; CHIT; CHITD |
| WB Predicted band size | 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CHIT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CHIT1抗体的代表性文献(虚构示例,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CHIT1 as a Biomarker in Gaucher Disease*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:研究验证了CHIT1抗体在戈谢病患者血浆中的检测效能,发现其活性显著升高,可作为疾病进展和治疗监测的生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-CHIT1 Antibodies in Chronic Inflammatory Disorders*
**作者**:Lee S, et al.
**摘要**:通过ELISA和免疫组化分析,证明CHIT1抗体可特异性识别炎症组织中巨噬细胞表达的几丁质酶1.提示其在慢性炎症病理中的作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a High-Sensitivity CHIT1 Detection Kit*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:开发了基于单克隆抗体的CHIT1定量检测试剂盒,灵敏度达pg/mL级别,适用于溶酶体储存疾病的早期诊断。
---
(注:以上文献为示例模型生成,实际引用需查询真实数据库如PubMed。)
The CHIT1 antibody targets chitotriosidase-1 (CHIT1), a 50 kDa glycosidase belonging to the human chitinase family. CHIT1 is primarily secreted by activated macrophages and plays a role in hydrolyzing chitin, a structural polysaccharide in fungi, parasites, and insects. Though humans lack endogenous chitin, CHIT1 is implicated in innate immune responses, potentially aiding in pathogen clearance and tissue remodeling. Elevated CHIT1 activity is associated with several pathologies, including Gaucher disease (a lysosomal storage disorder), idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and atherosclerosis, making it a biomarker for disease progression and macrophage activation.
CHIT1 antibodies are essential tools for research, enabling detection and quantification of CHIT1 in biological samples via techniques like ELISA, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry. These antibodies help elucidate CHIT1’s role in inflammatory and fibrotic pathways, particularly its contribution to macrophage-mediated tissue damage or repair. Recent studies also explore CHIT1’s dual role in metabolic syndromes and cancer, where its expression may influence disease mechanisms. Therapeutic interest in CHIT1 inhibition has grown, with antibodies aiding in validating drug candidates targeting chitinase activity. However, interpreting CHIT1 data requires caution due to genetic polymorphisms (e.g., the common 24-bp duplication mutation reducing enzyme activity) and cross-reactivity risks with homologous chitinases like AMCase. Overall, CHIT1 antibodies remain pivotal in advancing understanding of its biological and clinical significance.
×