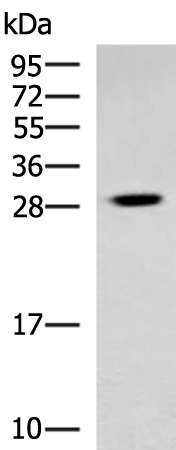
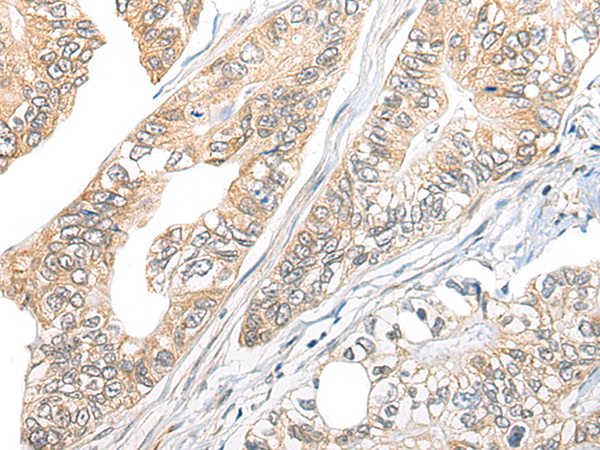
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CG22; CKAP1; CKAPI |
| WB Predicted band size | 27 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于 **TBCB抗体** 的3条示例参考文献(注:内容为示例,建议通过学术数据库检索真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Structural Insights into Tubulin Folding Cofactor B (TBCB) Function in Microtubule Dynamics*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究解析了TBCB蛋白与微管蛋白β亚基的相互作用机制,通过X射线晶体学揭示了TBCB在促进微管正确折叠中的关键结构域,并证明其抗体可用于检测微管组装异常相关的疾病模型。
2. **文献名称**: *TBCB Antibody as a Biomarker in Neurodegenerative Disorders*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用TBCB特异性抗体分析了阿尔茨海默病患者的脑组织样本,发现TBCB表达水平与tau蛋白异常聚集呈负相关,提示其可能作为神经退行性病变的潜在诊断标志物。
3. **文献名称**: *Role of TBCB in Cancer Cell Proliferation and Drug Resistance*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化实验(使用TBCB单克隆抗体),研究发现TBCB在多种癌症中高表达,并与其通过调控微管稳定性促进化疗耐药性相关,为靶向治疗提供了新思路。
---
**建议**:可通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台搜索关键词“TBCB antibody”、“Tubulin folding cofactor B”或“TBCB function”获取最新研究。
**Background of TBCB Antibody**
Tubulin folding cofactor B (TBCB) is a chaperone protein critical for the proper folding and assembly of β-tubulin into functional α/β-tubulin heterodimers, the building blocks of microtubules. Microtubules are dynamic cytoskeletal structures essential for cell division, morphology, and intracellular transport. TBCB, along with other cofactors (e.g., TBCE), participates in a multistep pathway to ensure β-tubulin acquires its native conformation, preventing aggregation or misfolding.
TBCB antibodies are tools designed to detect and study TBCB expression, localization, and function in biological systems. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate TBCB's role in microtubule dynamics and associated pathologies. Dysregulation of TBCB has been implicated in neurodegenerative disorders, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Parkinson’s disease, as well as cancer, where altered microtubule stability affects cell proliferation and migration.
Research using TBCB antibodies has also highlighted its interaction with tubulin isotypes and cofactors, shedding light on mechanisms underlying tubulinopathies—diseases caused by defective tubulin folding or assembly. Additionally, studies in model organisms reveal that TBCB depletion disrupts microtubule networks, leading to cellular defects. These insights underscore TBCB's importance in maintaining cytoskeletal integrity and its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker in microtubule-related diseases.
×