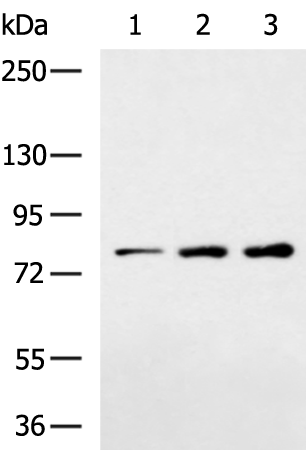
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
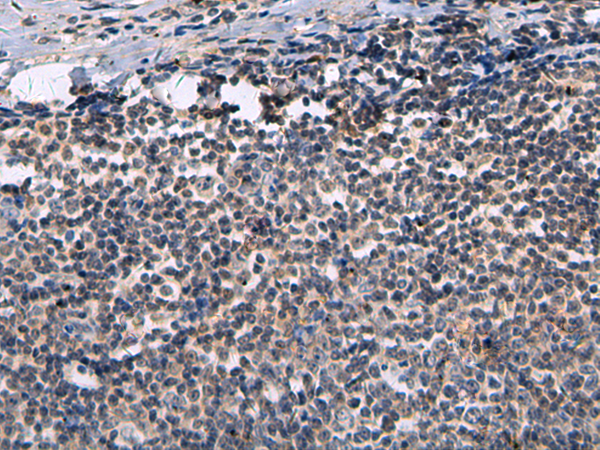
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HOD; CLC7; CLC-7; OPTA2; OPTB4; PPP1R63 |
| WB Predicted band size | 89 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CLCN7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CLCN7抗体相关的代表性文献摘要(基于公开研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Mutations in CLCN7 cause osteopetrosis in mice and humans*
**作者**: Kornak U, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次揭示了CLCN7基因突变导致小鼠和人类骨硬化症的机制。通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术使用CLCN7特异性抗体,证实突变导致破骨细胞溶酶体氯离子通道功能缺陷,阻碍骨吸收过程。
---
2. **文献名称**: *CLC-7 requires Ostm1 as a β-subunit to support bone resorption and lysosomal function*
**作者**: Lange PF, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用CLCN7抗体进行共免疫沉淀实验,发现CLCN7蛋白与Ostm1形成复合物,共同维持破骨细胞溶酶体酸化和骨吸收功能。抗体阻断实验进一步验证了二者在疾病中的相互作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Lysosomal storage and impaired autophagy in CLCN7-dependent osteopetrosis*
**作者**: Weinert S, et al.
**摘要**: 通过CLCN7抗体标记溶酶体膜,发现CLCN7缺陷导致溶酶体贮积和自噬功能障碍。研究强调了CLCN7抗体在追踪溶酶体形态变化中的应用,及其在神经退行性疾病中的潜在关联。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时需核对具体来源(如PubMed ID)。CLCN7抗体的研究多聚焦于骨代谢疾病和溶酶体功能领域,建议结合关键词"CLCN7 antibody"+"osteopetrosis"/"lysosome"检索最新文献。
The CLCN7 antibody targets the CLCN7 protein, a member of the CLC family of voltage-gated chloride channels/transporters. CLCN7 encodes the ClC-7 chloride channel, which forms a dimeric structure with two independent ion-conducting pores. Primarily localized in lysosomes and the ruffled border of osteoclasts, ClC-7 plays a critical role in lysosomal pH regulation and bone resorption by facilitating chloride ion transport. Mutations in the CLCN7 gene are linked to osteopetrosis, a rare genetic disorder characterized by increased bone density due to impaired osteoclast activity. Specifically, autosomal recessive osteopetrosis (ARO) and autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type 2 (ADO2) are associated with loss-of-function or dominant-negative mutations, respectively. Additionally, ClC-7 dysfunction may contribute to lysosomal storage disorders and neurodegenerative phenotypes.
CLCN7 antibodies are widely used in research to study protein expression, subcellular localization, and functional alterations in disease models. They enable detection of ClC-7 in tissues like bone, brain, and kidney via techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. These antibodies also aid in exploring therapeutic strategies targeting osteoclast activity or lysosomal function. However, challenges remain in distinguishing pathogenic mutations from benign variants and understanding tissue-specific regulatory mechanisms. Ongoing studies aim to clarify ClC-7's interactions with accessory proteins (e.g., OSTM1) and its role beyond ion transport, such as in cellular autophagy and signaling pathways.
×