| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
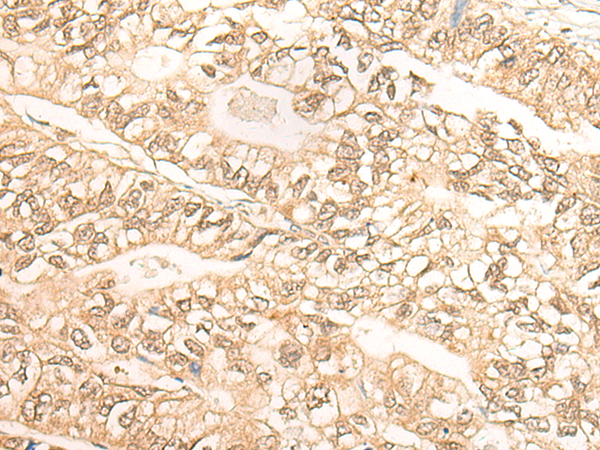
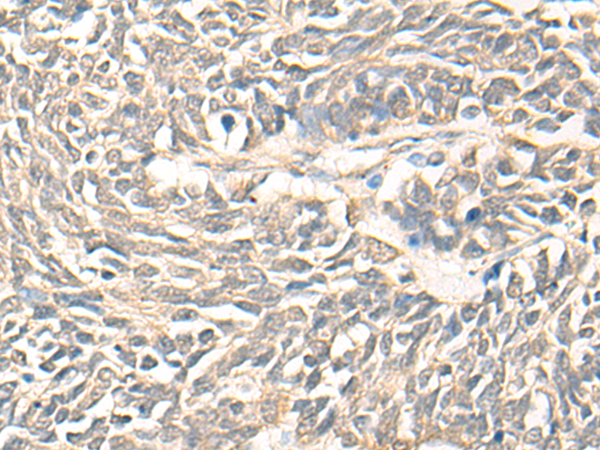
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DMC1H; LIM15; dJ199H16.1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DMC1抗体的3篇参考文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Cloning and characterization of the DMC1 gene from Arabidopsis thaliana*
**作者**: Klimyuk, V.I., Jones, J.D.G.
**摘要**: 该研究首次报道了拟南芥中DMC1基因的克隆,并制备了特异性多克隆抗体。通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证实DMC1蛋白在减数分裂早期阶段表达,且抗体能特异性识别植物细胞中与染色体联会相关的蛋白定位。
---
2. **文献名称**: *DMC1: A meiosis-specific yeast homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation, and cell cycle progression*
**作者**: Bishop, D.K., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用重组DMC1蛋白免疫小鼠制备单克隆抗体,发现DMC1在酵母减数分裂过程中与DNA双链断裂修复直接相关。抗体被用于免疫沉淀和共聚焦显微镜分析,揭示了DMC1在联会复合体动态组装中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Distinct roles of RAD51 and DMC1 in the interference-sensitive and -independent recombination*
**作者**: Tsubouira, T., Haber, J.E.
**摘要**: 通过比较RAD51与DMC1在减数分裂重组中的功能差异,研究团队利用DMC1抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和免疫共定位分析,发现DMC1特异性地参与干扰敏感型重组事件,且其抗体在区分同源重组路径中具有高特异性。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需核对具体论文信息。如需精准文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“DMC1 antibody”为关键词检索近年研究。
DMC1 (DNA Meiotic Recombinase 1) is a conserved eukaryotic protein essential for homologous recombination during meiosis, specifically facilitating the repair of double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA. As a meiosis-specific homolog of the bacterial RecA protein, DMC1 promotes strand exchange between homologous chromosomes, ensuring accurate chromosome pairing and crossover formation. This process is critical for genetic diversity and proper chromosome segregation in gametes.
Antibodies targeting DMC1 are widely used in research to study meiosis dynamics, particularly in germ cells. They enable the visualization and quantification of DMC1 foci—microscopic sites where recombination occurs—on meiotic chromosomes via techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, or immunohistochemistry. Such studies have elucidated DMC1's role in fertility, its interaction with co-factors (e.g., RAD51. BRCA2), and its dysregulation in conditions like infertility or genomic instability.
Commercial DMC1 antibodies are typically raised against conserved epitopes, often validated in model organisms (e.g., mice, plants, yeast). Researchers rely on these tools to investigate meiotic defects, evolutionary conservation of recombination mechanisms, and potential links to reproductive disorders. Recent applications extend to CRISPR-edited cell lines or single-cell genomics, underscoring DMC1's enduring relevance in molecular and reproductive biology.
×