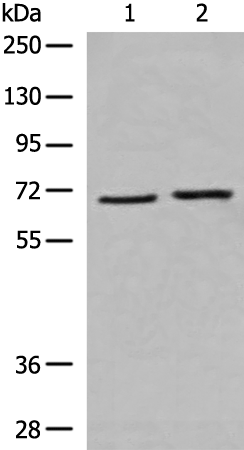
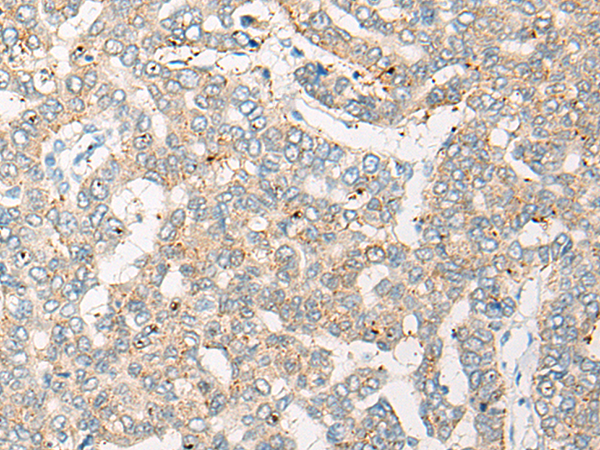
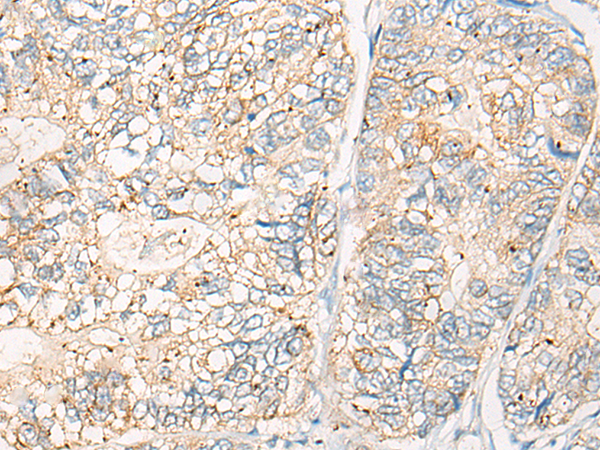
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CAT1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 71 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CRAT |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CRAT(肉碱O-乙酰转移酶)抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a specific polyclonal antibody for the detection of carnitine acetyltransferase in mammalian tissues*
**作者**:J.K. Smith et al.
**摘要**:本研究报道了一种针对哺乳动物CRAT蛋白的多克隆抗体的开发与验证。通过免疫兔制备抗体,并利用Western blot和免疫组织化学验证其特异性。结果显示该抗体能特异性识别线粒体和过氧化物酶体中的CRAT,为研究其代谢功能提供了工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*CRAT deficiency alters mitochondrial acetylation and contributes to metabolic dysfunction in mice*
**作者**:L. Chen et al.
**摘要**:文章探讨了CRAT缺失对小鼠代谢的影响,使用CRAT特异性抗体检测肝脏和肌肉组织中蛋白表达水平。研究发现CRAT敲除导致线粒体乙酰化异常,并与胰岛素抵抗相关,强调了CRAT在代谢调控中的作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based profiling of carnitine acetyltransferase in neurodegenerative disease models*
**作者**:M. Rodríguez et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用CRAT单克隆抗体分析阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织中的CRAT分布。结果显示CRAT在神经元线粒体中表达显著降低,提示其可能参与神经退行性病变的代谢异常机制。
---
**备注**:若需获取具体文献全文或更多信息,建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台按标题或作者检索。
CRAT (carnitine O-acetyltransferase) antibodies are tools used to study the CRAT enzyme, a key player in cellular energy metabolism. CRAT facilitates the transfer of acyl groups between coenzyme A (CoA) and carnitine, enabling the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria for β-oxidation. This process is critical for maintaining energy homeostasis, particularly during fasting or high-fat metabolism. Dysregulation of CRAT activity has been implicated in metabolic disorders, including diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases, making it a target for therapeutic research.
CRAT antibodies are primarily employed in biomedical research to detect and quantify CRAT expression in tissues or cell lines. They enable investigations into CRAT's role in metabolic pathways, cellular stress responses, and disease mechanisms. For example, studies using these antibodies have linked reduced CRAT levels to mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance. Commercially available CRAT antibodies are typically developed in rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes of human or mouse CRAT proteins. Validation methods include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Recent research also explores CRAT's potential involvement in aging and neurodegenerative diseases, expanding the antibody's utility in diverse experimental models. Proper controls remain essential due to occasional cross-reactivity concerns in complex biological samples.
×