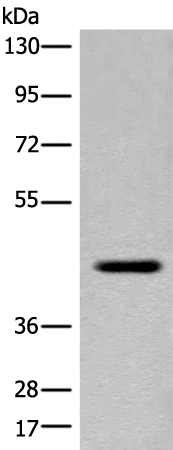
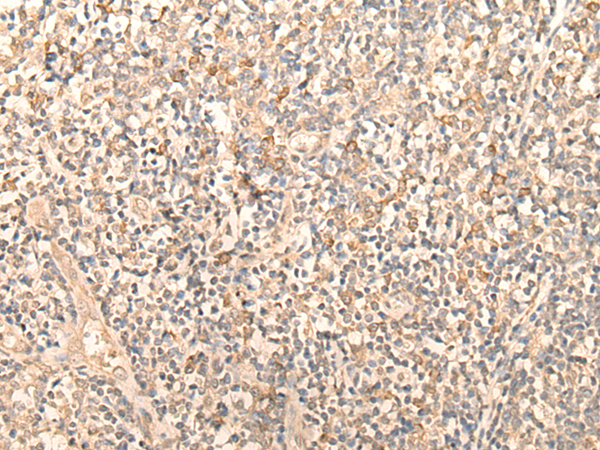
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NET20; FAM105A |
| WB Predicted band size | 42 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human OTULINL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于OTULIN抗体的3篇代表性文献,包含文献名称、作者和摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*OTULIN restricts Met1-linked ubiquitination to control innate immune signaling*
**作者**:Damgaard, R.B. et al. (2013)
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了OTULIN作为去泛素化酶,特异性水解Met1(线性)泛素链,负调控NF-κB信号通路。文中通过OTULIN抗体验证其在细胞中的表达,并发现其与LUBAC复合物(HOIP、HOIL-1)的相互作用,揭示了OTULIN在先天免疫中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*OTULIN deficiency causes autoinflammatory syndrome by impairing NF-κB antiapoptotic signaling*
**作者**:Rivkin, E. et al. (2017)
**摘要**:研究通过OTULIN基因敲除小鼠模型,结合OTULIN抗体检测蛋白表达,证明OTULIN缺失导致细胞凋亡抵抗和过度炎症反应。该文献揭示了OTULIN在维持细胞稳态中的重要性,并提出了其突变与人类自身炎症性疾病的关联。
---
3. **文献名称**:*OTULIN antagonizes LUBAC signaling by specifically hydrolyzing Met1-linked polyubiquitin chains*
**作者**:Heger, K. et al. (2018)
**摘要**:本文利用OTULIN抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,证实OTULIN通过拮抗LUBAC介导的Met1泛素化,调控TNFα诱导的炎症信号。研究还发现OTULIN的酶活缺失会导致过度炎症反应,为靶向OTULIN的抗体在疾病治疗中的应用提供了理论基础。
---
如需具体文献链接或实验细节,可进一步补充说明。
OTULIN (OTU deubiquitinase with linear linkage specificity) is a deubiquitinating enzyme that specifically hydrolyzes linear (Met1-linked) ubiquitin chains, crucial regulators of NF-κB signaling and inflammatory responses. It binds to the LUBAC (linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex) to maintain homeostasis by counteracting LUBAC-mediated ubiquitination. Dysregulation of OTULIN is linked to autoinflammatory diseases, immune disorders, and cancer. For instance, biallelic OTULIN mutations cause OTULIN-related autoinflammatory syndrome (ORAS), characterized by systemic inflammation. OTULIN also modulates cell death pathways and is implicated in microbial infection responses.
OTULIN antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions. They enable detection via Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry, aiding research on its role in immune regulation and disease. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are used to explore OTULIN's involvement in NF-κB signaling, apoptosis, and inflammasome activation. Recent studies also highlight its potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in cancers with dysregulated ubiquitination pathways. Validated antibodies ensure specificity for linear ubiquitin chain-related studies, distinguishing OTULIN from other deubiquitinases. Research using these antibodies enhances understanding of ubiquitin-dependent signaling and supports drug development for inflammation-related pathologies.
×