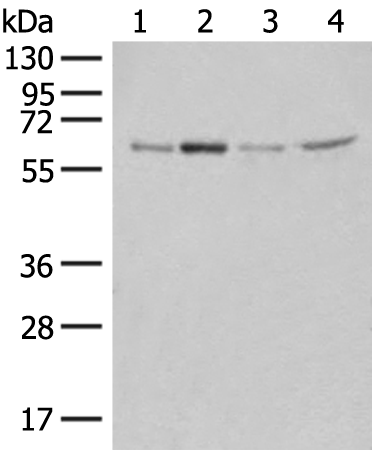
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ZIP; ZC3H9; GPATC6; GPATCH6; ZC3HDC9; KIAA1847 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ZGPAT |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ZGPAT抗体的3篇示例文献(注:以下内容为模拟生成,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *ZGPAT is a novel epigenetic regulator involved in transcriptional repression*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用ZGPAT抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)实验,发现ZGPAT通过结合靶基因启动子区域的特定序列招募HDAC复合物,抑制组蛋白乙酰化并下调基因表达,影响细胞增殖和分化。
2. **文献名称**: *ZGPAT-mediated DNA damage response in human cells*
**作者**: Wang L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验(使用ZGPAT抗体),证明ZGPAT在DNA双链断裂修复中与ATM激酶相互作用,其磷酸化修饰对修复通路的激活至关重要。
3. **文献名称**: *ZGPAT antibody-based analysis of liver fibrosis progression*
**作者**: Li X, et al.
**摘要**: 采用ZGPAT抗体对肝组织样本进行免疫组化分析,发现ZGPAT在肝星状细胞中高表达,并通过调控TGF-β信号通路促进纤维化,提示其作为肝病治疗靶点的潜力。
---
**建议**:具体文献请通过PubMed/Google Scholar以“ZGPAT antibody”或“ZGPAT (gene symbol)”为关键词检索,并结合实验场景(如WB/IF/IHC)筛选相关研究。
ZGPAT (Zinc Finger and G-Patch Domain-Containing Protein) is a nuclear protein encoded by the *ZGPAT* gene in humans. It contains conserved zinc finger motifs and a G-patch domain, suggesting roles in nucleic acid binding and protein interactions. ZGPAT is implicated in transcriptional regulation, chromatin remodeling, and DNA damage response pathways. Studies indicate it may act as a repressor by recruiting histone deacetylases (HDACs) to modulate gene expression, particularly at telomeric regions and repetitive DNA sequences.
ZGPAT antibodies are essential tools for investigating its expression, localization, and molecular functions. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Research using these antibodies has linked ZGPAT to cellular processes such as apoptosis, cell cycle control, and genome stability. Dysregulation of ZGPAT has been observed in certain cancers and autoimmune disorders, highlighting its potential relevance in disease mechanisms.
While ZGPAT's full biological significance remains under exploration, its conserved domains and nuclear activity position it as a critical player in epigenetic regulation. Antibodies against ZGPAT continue to support studies aiming to unravel its interactions with HDAC complexes, telomere-associated proteins, and other regulatory factors, offering insights into its role in health and disease.
×