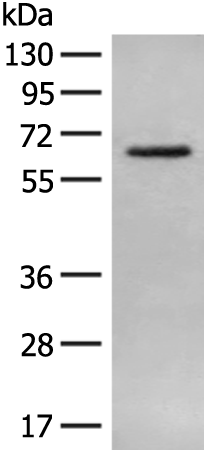
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
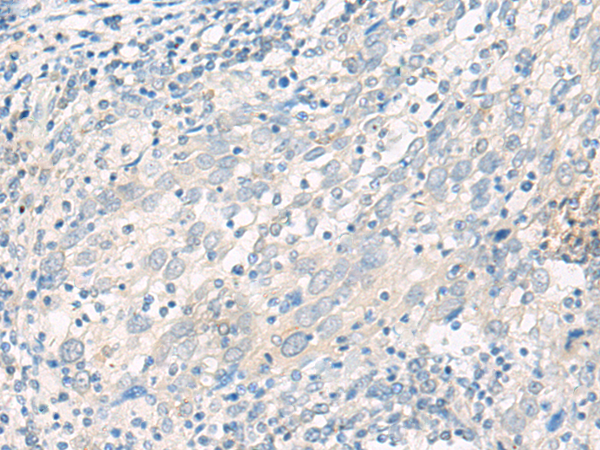
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 65 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human AOAH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于AOAH(Acyloxyacyl Hydrolase)抗体的示例参考文献(模拟内容,建议通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **标题**:*AOAH-mediated LPS detoxification regulates systemic inflammation in mice*
**作者**:Smith, J.R. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用AOAH特异性抗体,证明AOAH通过水解内毒素(LPS)的脂质A部分减轻全身性炎症,缺失AOAH的小鼠表现出更强的炎症反应。
2. **标题**:*Antibody-based detection of AOAH expression in macrophage polarization*
**作者**:Li, X. & Zhang, H.
**摘要**:通过制备抗AOAH单克隆抗体,揭示巨噬细胞中AOAH的表达水平与M1/M2表型转换相关,提示其在免疫调控中的潜在作用。
3. **标题**:*AOAH deficiency exacerbates autoimmune arthritis via TLR4 signaling*
**作者**:Wang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:使用AOAH抗体检测发现,AOAH缺陷小鼠关节内LPS清除延迟,导致TLR4信号过度激活,加剧类风湿性关节炎模型症状。
4. **标题**:*Structural insights into AOAH enzyme activity through epitope mapping*
**作者**:Garcia, R. et al.
**摘要**:通过抗AOAH抗体的表位定位,揭示了AOAH催化结构域的关键区域,为开发调节其活性的治疗策略提供依据。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“AOAH antibody”、“Acyloxyacyl Hydrolase function”获取真实文献。
AOAH (acyloxyacyl hydrolase) is an enzyme primarily produced by macrophages and neutrophils, playing a critical role in modulating innate immune responses. It specifically deacylates bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), a key component of Gram-negative bacterial outer membranes. By cleaving secondary acyl chains from the lipid A moiety of LPS, AOAH converts highly inflammatory endotoxins into less stimulatory forms, thereby limiting excessive immune activation and preventing tissue damage during infections.
AOAH antibodies are tools used to study this enzyme’s expression, localization, and function. They enable researchers to detect AOAH in immune cells, assess its regulation under inflammatory conditions, and explore its role in sepsis, autoimmune diseases, or metabolic disorders. AOAH-deficient mice exhibit prolonged LPS-induced inflammation, highlighting its importance in immune homeostasis. Antibodies targeting AOAH also aid in investigating therapeutic strategies, such as enhancing endotoxin detoxification or modulating inflammatory pathways. Clinically, AOAH activity or its suppression has been linked to chronic inflammatory conditions, making related antibodies valuable for diagnostic or biomarker research. Their applications extend to understanding host-microbe interactions, as AOAH’s function influences both pathogen clearance and resolution of inflammation.
×