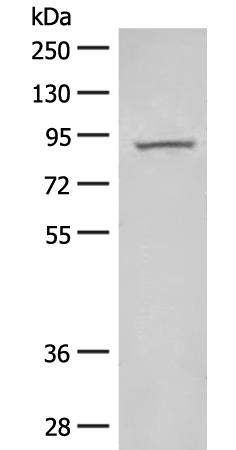
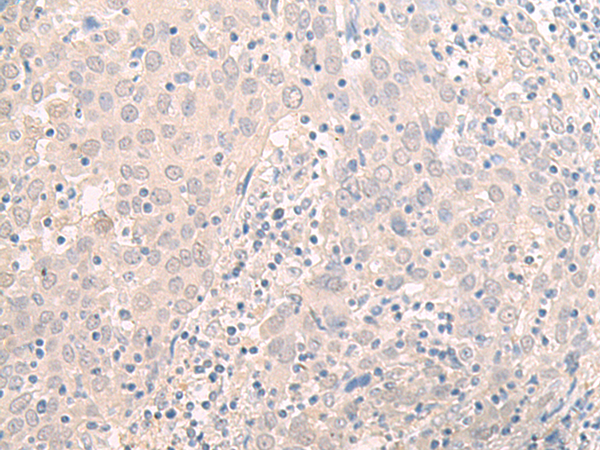
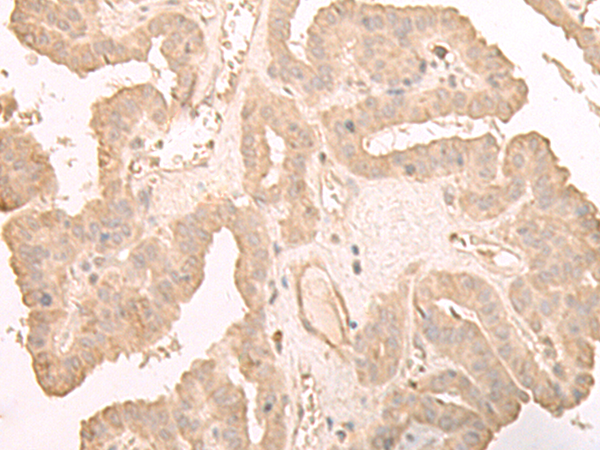
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/40-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HK2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 83 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human HOOK2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HOOK2抗体的3篇示例参考文献(请注意,以下内容为示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
1. **文献名称**: "HOOK2 regulates cargo-specific dynein function in primary cilia formation"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示了HOOK2通过结合细胞质动力蛋白(dynein)调控初级纤毛形成的过程,其抗体用于验证HOOK2在纤毛基部的定位及与运输复合物的相互作用。
2. **文献名称**: "HOOK2 antibody validation in spermatogenesis: a role in acrosome biogenesis"
**作者**: Lee B, et al.
**摘要**: 利用HOOK2特异性抗体,研究发现其在精子形成过程中调控顶体发育,HOOK2缺失导致小鼠模型中出现精子形态异常和不育表型。
3. **文献名称**: "HOOK2 interacts with PCM1 and modulates centriolar satellite dynamics"
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(使用HOOK2抗体)和活细胞成像,证明HOOK2与PCM1蛋白相互作用,影响中心粒卫星的运输及细胞分裂稳定性。
**建议**:实际研究中,可通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“HOOK2 antibody”及“HOOK2 function”为关键词检索,重点关注抗体应用场景(如Western blot、免疫荧光)及功能机制研究。
The HOOK2 antibody is a tool used to detect HOOK2. a member of the HOOK protein family, which plays critical roles in intracellular trafficking and organelle positioning. HOOK proteins are adaptor molecules that mediate interactions between motor proteins, cargo vesicles, and microtubules. Specifically, HOOK2 contains an N-terminal microtubule-binding domain, a central coiled-coil region for dimerization, and a C-terminal domain that interacts with cargo or regulatory proteins. It is implicated in endosomal trafficking, lysosomal positioning, and ciliogenesis by linking organelles to dynein-dynactin motor complexes for retrograde transport along microtubules.
HOOK2 is ubiquitously expressed but shows enriched activity in tissues with high secretory or endocytic demands, such as neurons and polarized epithelial cells. Dysregulation of HOOK2 has been associated with ciliopathies, cancer metastasis, and neurological disorders, underscoring its importance in cellular homeostasis. Antibodies targeting HOOK2 are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study its localization, expression levels, and interactions in both physiological and pathological contexts. Commercial HOOK2 antibodies are typically validated for specificity using knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown. Research utilizing these antibodies has advanced understanding of HOOK2's role in Golgi organization, autophagy, and cell division, making it a key reagent in cell biology and disease mechanism studies.
×