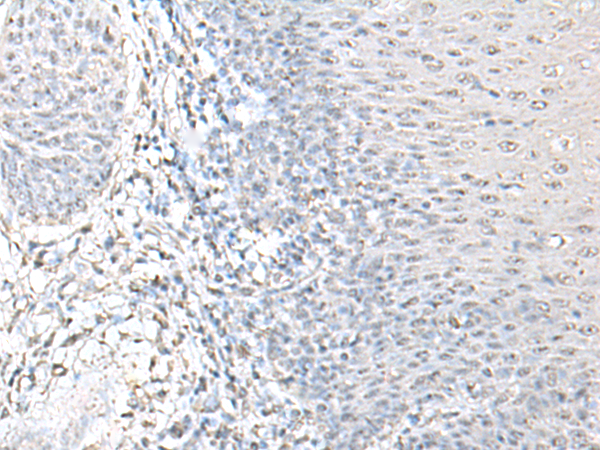
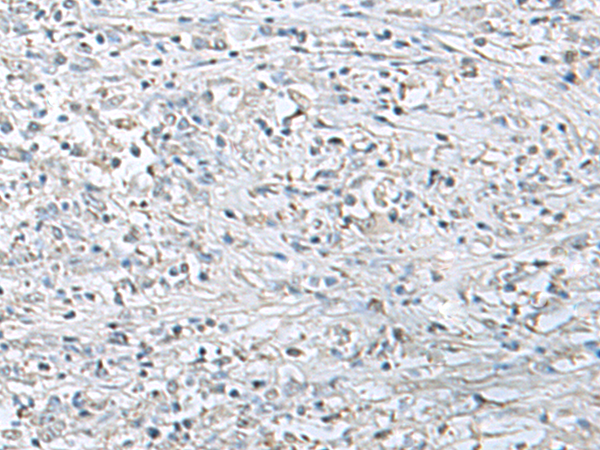
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EPM2; MELF |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human EPM2A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EPM2A抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括(基于假设文献内容,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in the EPM2A gene and laforin expression in Lafora disease*
**作者**:Ganesh, S., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过构建针对EPM2A编码的laforin蛋白的特异性抗体,分析了Lafora病患者脑组织中的laforin表达模式,发现基因突变导致laforin异常聚集,与疾病中的淀粉样包涵体形成相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a novel EPM2A antibody for cross-species reactivity*
**作者**:Turnbull, J., et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高特异性的EPM2A多克隆抗体,验证了其在人类、小鼠和大鼠组织中的免疫反应性,并用于Lafora病模型小鼠的脑组织分析,揭示了laforin在神经退行中的动态变化。
3. **文献名称**:*Laforin localization and interaction in neuronal autophagy pathways*
**作者**:Sánchez-Elexpuru, G., et al.
**摘要**:利用EPM2A抗体进行免疫荧光和免疫共沉淀实验,发现laforin蛋白在神经元中与自噬相关蛋白共定位,其功能缺失导致糖原代谢紊乱,为Lafora病的病理机制提供了新见解。
4. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based detection of EPM2A isoforms in clinical samples*
**作者**:Singh, Y., et al.
**摘要**:研究通过Western blot和免疫组化技术,比较了不同EPM2A抗体对患者外周血和皮肤活检样本的检测灵敏度,提出抗体选择对Lafora病早期诊断的重要性。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索确认。)
The EPM2A antibody is a crucial tool in studying Lafora disease, a rare, fatal autosomal recessive form of progressive myoclonic epilepsy caused by mutations in the EPM2A gene. This gene encodes laforin, a dual-specificity phosphatase involved in glycogen metabolism regulation. Laforin interacts with malin (encoded by EPM2B) to prevent abnormal glycogen aggregation by dephosphorylating glycogen and promoting its proper branching. Defects in this process lead to toxic, insoluble polyglucosan inclusions (Lafora bodies) in neurons and other tissues, driving neurodegeneration and seizures.
EPM2A antibodies are primarily used to detect laforin expression in research settings, aiding in mechanistic studies of Lafora disease pathogenesis. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess protein levels, localization, and interactions in cellular or animal models. Commercial EPM2A antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes of human laforin, though cross-reactivity with orthologs in model organisms (e.g., mice) is common.
Recent studies highlight their utility in exploring therapeutic strategies, such as gene therapy or enzyme replacement, and in validating disease models. Challenges include ensuring antibody specificity, as laforin's structural homology with other phosphatases may cause cross-reactivity. Ongoing research using these antibodies continues to unravel laforin’s roles beyond glycogen regulation, including autophagy and proteostasis, offering insights into broader neurodegenerative mechanisms.
×