| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
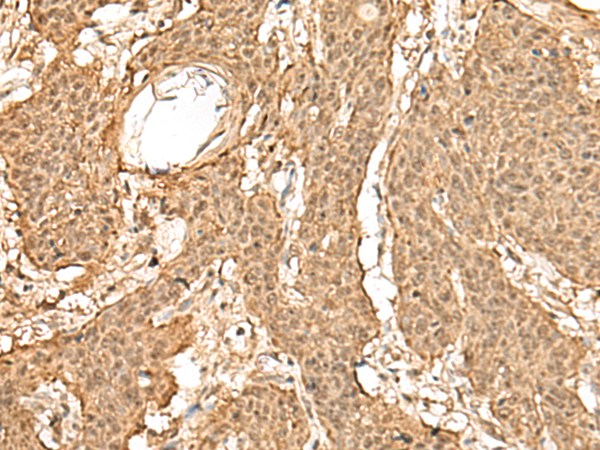
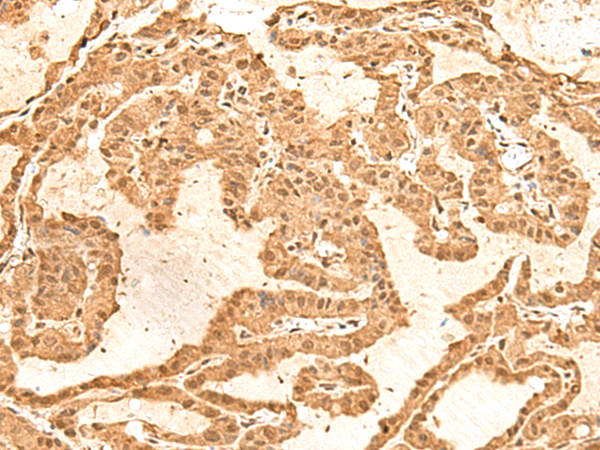
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TIP; TIP41; TIPRL1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TIPRL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TIPRL抗体的参考文献,提供文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*TIPRL, a novel protein that modulates the phosphoregulation of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway*
**作者**:Kim ST, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了TIPRL作为mTOR信号通路调控因子,通过抑制PP2A磷酸酶活性影响细胞生长。研究中使用TIPRL抗体进行Western blot和免疫共沉淀,验证了TIPRL与PP2A的相互作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into TIPRL-mediated inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A*
**作者**:Xu Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析TIPRL与PP2A-C亚基的结合结构,揭示其抑制PP2A活性的分子机制。实验中利用TIPRL抗体进行免疫荧光定位,证实其在细胞质中的分布与功能关联。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Dysregulation of TIPRL expression correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:探讨TIPRL在肝细胞癌中的临床意义,发现其高表达与患者生存率降低相关。通过TIPRL抗体进行免疫组化分析,证实其在肿瘤组织中的异常上调与mTOR通路过度激活有关。
---
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时需以具体论文内容为准。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“TIPRL antibody”或“TIPRL function”检索最新研究。)
TIPRL (TOR Signaling Pathway Regulator-like Protein) is a conserved eukaryotic protein implicated in regulating the TOR (Target of Rapamycin) signaling pathway, a central hub for cell growth, proliferation, and autophagy. First identified in yeast, TIPRL homologs in mammals interact with protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), a key phosphatase involved in diverse cellular processes. TIPRL acts as a PP2A inhibitory regulator by binding to its catalytic subunit, modulating phosphatase activity and influencing downstream targets of mTORC1 (mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1). This interaction links TIPRL to nutrient sensing, stress responses, and cancer progression. Studies show TIPRL overexpression in several cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, lung cancer, and cervical cancer, where it promotes tumor growth and chemoresistance by dysregulating apoptosis and autophagy.
TIPRL antibodies, typically polyclonal or monoclonal reagents raised against specific epitopes (e.g., human TIPRL residues), are essential tools for detecting TIPRL expression in tissues or cell lines via Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, or immunofluorescence. They aid in elucidating TIPRL’s role in mTOR pathway regulation, cancer biology, and therapeutic targeting. Recent research also explores TIPRL’s involvement in viral infections and neurological disorders, highlighting its broad functional relevance. Validated antibodies with high specificity are critical, as TIPRL shares homology with other phosphatases. Commercial antibodies often target conserved regions (e.g., C-terminal domains) and are tested for cross-reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat).
×