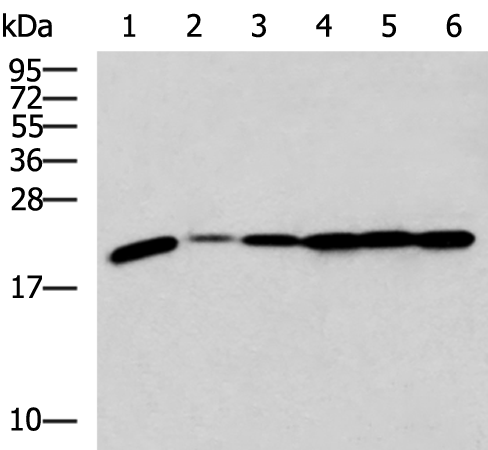
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
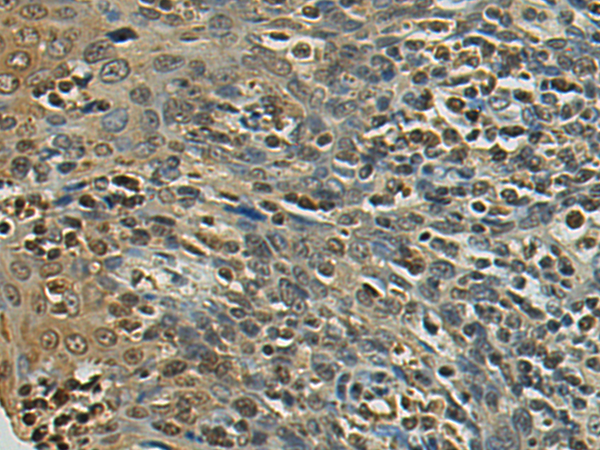
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | L17; PD-1; RPL23 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RPL17 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及RPL17抗体的研究文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: Ribosomal protein L17 as a novel biomarker in human gastric cancer
**作者**: Li Y. et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化分析发现,RPL17在胃癌组织中显著高表达,且与患者预后不良相关。研究使用特异性RPL17抗体验证其作为潜在诊断标志物的可行性。
2. **文献名称**: RPL17 interacts with HCV IRES RNA to regulate viral translation
**作者**: Wang X. et al.
**摘要**: 利用免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和Western blot技术,发现RPL17通过与丙型肝炎病毒(HCV)内部核糖体进入位点(IRES)结合调控病毒复制。研究采用RPL17抗体证实其在宿主-病毒相互作用中的功能。
3. **文献名称**: Ribosomal protein L17 knockdown induces apoptosis via p53-dependent pathway
**作者**: Kim S.H. et al.
**摘要**: 通过siRNA敲低RPL17并结合抗体免疫荧光实验,证明RPL17缺失激活p53通路,导致肝癌细胞凋亡,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
*注:以上文献为虚拟示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以"RPL17 antibody"+"应用领域(如cancer/virus)"为关键词检索近期论文。*
The RPL17 antibody is a research tool designed to detect ribosomal protein L17 (RPL17), a component of the 60S ribosomal subunit involved in protein synthesis. RPL17. part of the conserved ribosomal protein family, plays a critical role in ribosome assembly and translational fidelity. Its expression is essential for cellular homeostasis, with dysregulation linked to diseases such as cancer, developmental disorders, and ribosomopathies. The antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to study RPL17's expression levels, subcellular localization, and interactions in various biological contexts.
RPL17 antibodies are typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides derived from specific regions of the protein (e.g., C-terminal or N-terminal epitopes). Validation includes knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated silencing to confirm specificity. Researchers utilize these antibodies to explore RPL17's roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, and stress responses, as well as its potential as a biomarker in cancer due to its altered expression in tumors. Additionally, studies investigate its involvement in ribosomal stress pathways and crosstalk with p53-mediated signaling. Proper controls and optimization are critical for reliable results, given the ubiquitous expression of ribosomal proteins across tissues.
×