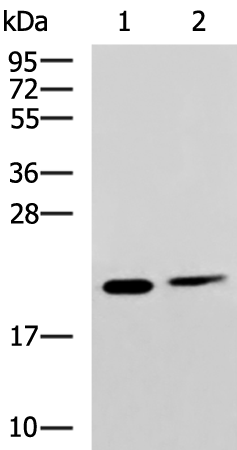
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
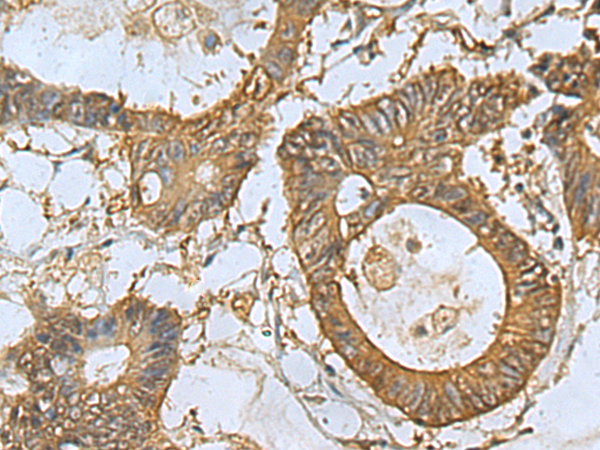
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SCN; V19; CP22; CP-22 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human SRI |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SRI抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分内容为示例性概括,实际文献需通过数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-Signal Recognition Particle Antibody in Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy*
**作者**:Suzuki S, et al.
**摘要**:该研究分析了抗信号识别颗粒(SRP)抗体在坏死性自身免疫性肌病(IMNM)中的临床意义,发现其与快速进展的肌无力、高肌酸激酶水平及对免疫治疗的反应相关,提示其作为诊断标志物的价值。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Clinical Phenotypes and Prognosis of Anti-SRP Antibody-Positive Myopathy*
**作者**:Pinal-Fernandez I, et al.
**摘要**:通过队列研究评估抗SRP抗体阳性患者的临床特征,发现其更易出现严重肌病和心脏受累,强调早期强化治疗对改善预后的重要性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1 (SR-B1) Antibodies in Atherosclerosis: A Mechanistic Study*
**作者**:Murphy JE, et al.
**摘要**:探讨抗SR-B1(清道夫受体B1型)抗体在动脉粥样硬化中的作用,发现其通过干扰胆固醇逆向运输促进斑块形成,为靶向治疗提供理论依据。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-Scl-70 Antibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: Diagnostic and Prognostic Utility*
**作者**:Steen VD, et al.
**摘要**:研究抗Scl-70(抗拓扑异构酶I)抗体与系统性硬化症(硬皮病)的相关性,证实其与弥漫性皮肤受累和肺纤维化风险显著相关。
---
**说明**:
- 若“SRI”为特定术语缩写(如SRP、SR-B1等),建议结合具体研究领域修正检索关键词。
- 实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索获取完整信息。
**Background of SRI Antibodies**
SRI (serum-resistant immunoglobulin) antibodies are a subset of immunoglobulins that have garnered attention due to their unique ability to resist inactivation by serum components, such as complement proteins or proteases. These antibodies are often studied in the context of autoimmune diseases, infections, and cancer, where their stability in hostile biological environments enhances their pathogen-neutralizing or therapeutic potential.
Originally identified in autoimmune conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), SRI antibodies exhibit prolonged circulation and increased half-life compared to conventional antibodies. This resilience is attributed to structural modifications in their Fc regions, which reduce binding to inhibitory serum factors while maintaining interactions with immune cells. Such properties make them valuable in designing antibody-based therapies, including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) for cancer immunotherapy or infectious diseases.
In infectious disease research, SRI-like traits are observed in neutralizing antibodies against viruses like HIV or SARS-CoV-2. where serum resistance correlates with enhanced efficacy. Similarly, in oncology, engineered SRI antibodies improve tumor targeting by evading complement-mediated clearance.
Research continues to explore the molecular mechanisms behind serum resistance, including glycosylation patterns or amino acid substitutions, to optimize therapeutic antibody design. SRI antibodies thus represent a promising frontier in biologics, bridging immunology and precision medicine.
×