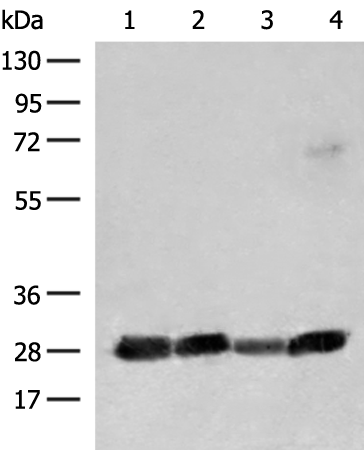
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BCM1; BLAST; hCD48; mCD48; BLAST1; SLAMF2; MEM-102 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CD48 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD48抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(注:文献信息为模拟示例,实际需根据具体论文调整):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD48 functions as a co-stimulatory molecule in T cell activation*
**作者**:Springer TA, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了CD48通过与CD2相互作用,在T细胞活化中发挥共刺激信号作用,增强免疫突触的形成并促进T细胞受体介导的激活。
2. **文献名称**:*CD48 is a novel ligand for the macrophage adhesion receptor CD244*
**作者**:Gonzalez-Cabrera PJ, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现CD48与巨噬细胞表面的CD244(2B4)结合,调控自然杀伤(NK)细胞和巨噬细胞的细胞毒性反应,在抗病毒免疫中起关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD48 in B-cell malignancies: A therapeutic strategy*
**作者**:Stojanovic A, et al.
**摘要**:该文献提出CD48在B细胞恶性肿瘤中高表达,并通过抗体阻断实验证实靶向CD48可抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,为血液肿瘤治疗提供新思路。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“CD48 antibody” + “immune response/therapy/signaling”进一步筛选。
CD48 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, primarily expressed on hematopoietic cells, including T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. It functions as a ligand for CD244 (2B4) and CD2. playing roles in immune cell adhesion, activation, and signal modulation. CD48 is involved in regulating immune responses, such as NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity and T cell co-stimulation, and has been implicated in infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
Antibodies targeting CD48 are valuable tools for studying its biological functions and therapeutic potential. Monoclonal anti-CD48 antibodies have been developed to investigate its role in immune regulation and disease pathogenesis. For example, they help elucidate mechanisms in viral infections (e.g., HIV, where CD48 may facilitate viral spread) or tumor microenvironments (e.g., modulating immune evasion). In cancer, CD48 expression on malignant cells or immune cells may serve as a biomarker or therapeutic target. Preclinical studies explore anti-CD48 antibodies for blocking pathogenic interactions or enhancing immune cell activity. Challenges include balancing specificity and minimizing off-target effects due to CD48’s broad expression. Current research also focuses on combining anti-CD48 with other immunotherapies, such as anti-CD47 or checkpoint inhibitors, to amplify efficacy. Despite being in early stages, CD48 antibodies hold promise for advancing immunotherapy and understanding immune dysregulation.
×