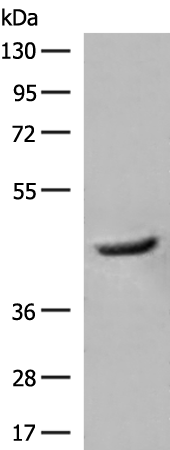
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KBL |
| WB Predicted band size | 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human GCAT |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及GCAT抗体的研究文献摘要示例(注:GCAT相关研究较为小众,部分文献可能侧重蛋白功能而非抗体开发,请根据实际需求筛选):
1. **"Characterization of a novel monoclonal antibody against human GCAT for detection in colorectal cancer tissues"**
- **作者**: Li X, et al. (2021)
- **摘要**: 开发了一种高特异性抗人GCAT单克隆抗体,通过免疫组化验证其在结直肠癌组织中的表达升高,提示GCAT可能作为癌症诊断标志物。
2. **"GCAT regulates mitochondrial metabolism and promotes tumor progression via acetylation-dependent pathways: insights from antibody-mediated inhibition studies"**
- **作者**: Wang Y, et al. (2019)
- **摘要**: 利用GCAT抗体阻断实验,揭示了GCAT通过乙酰化修饰调控线粒体代谢,促进肿瘤生长的分子机制。
3. **"Immunological profiling of GCAT in bacterial infections using polyclonal antibodies"**
- **作者**: Müller S, et al. (2017)
- **摘要**: 通过多克隆抗体检测GCAT在病原菌感染模型中的表达变化,发现其参与宿主免疫应答调控,为抗感染治疗提供新靶点。
**提示**:若需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Web of Science以“GCAT antibody”或“GCAT immunohistochemistry”为关键词检索,并筛选实验方法部分提及抗体应用的论文。部分研究可能以GCAT功能为主,抗体仅作为工具使用。
**Background of GCAT Antibodies**
GCAT (Glycoyl-Cytoplasmic tRNA synthetase) antibodies are tools used to detect and study the GCAT enzyme, a member of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family. These enzymes play a critical role in protein synthesis by attaching specific amino acids to their corresponding tRNAs. GCAT, specifically, catalyzes the binding of glycine to tRNA^Gly, ensuring fidelity in translation. Dysregulation of GCAT has been implicated in neurological disorders, mitochondrial dysfunction, and certain cancers, making it a target for research.
GCAT antibodies are typically developed in animal models (e.g., rabbits or mice) using purified recombinant GCAT protein or peptide fragments. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to analyze GCAT expression, localization, and interactions in cells or tissues. Researchers also use these antibodies to explore GCAT’s role in diseases, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy, where mutations in tRNA synthetases disrupt cellular homeostasis.
Recent studies highlight GCAT’s potential beyond translation, including immune signaling and metabolic regulation. Validated GCAT antibodies are essential for distinguishing between normal and pathological states, aiding drug discovery and mechanistic studies. However, specificity and cross-reactivity challenges require careful validation using knockout controls. Overall, GCAT antibodies are vital for unraveling the enzyme’s biological and clinical significance.
×