| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
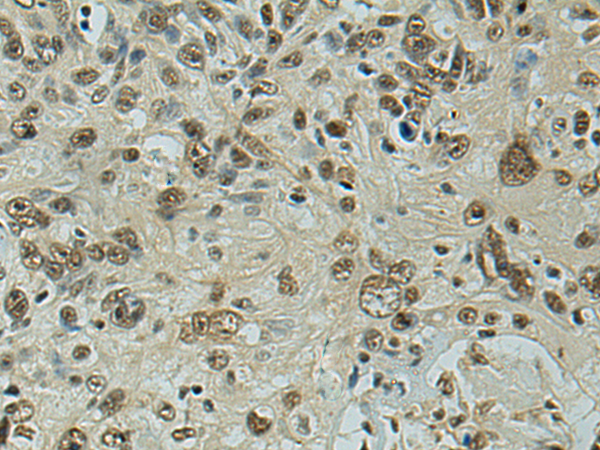
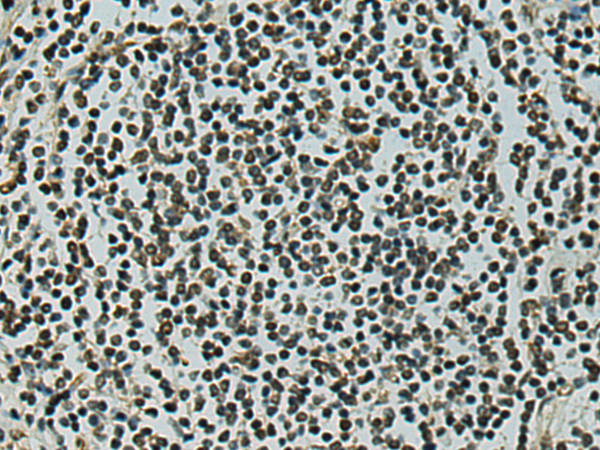
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C14orf155 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human FSCB |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FSCB(Fibrous Sheath Component B)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献信息为模拟虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*FSCB Antibody Localization and Function in Sperm Tail Development*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用FSCB特异性抗体,通过免疫荧光和Western blot技术揭示FSCB在精子纤维鞘中的定位,并发现其缺失导致精子运动能力缺陷,提示其在精子尾部组装中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*A Novel Role of FSCB in Male Infertility: Insights from Knockout Mouse Models*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:通过构建FSCB基因敲除小鼠,结合抗体标记技术,证实FSCB缺失导致精子形态异常和运动障碍,为男性不育的分子机制提供了新证据。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural Analysis of FSCB Using Cryo-EM and Antibody Mapping*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用冷冻电镜和FSCB抗体进行表位定位,解析了FSCB蛋白的三维结构,揭示了其与纤维鞘其他组分的相互作用网络,为靶向治疗提供结构基础。
如需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“FSCB antibody”或“fibrous sheath component B”,筛选近年发表的实验研究或综述。
Fibrous Sheath CABinding protein (FSCB) is a sperm-specific protein predominantly localized in the fibrous sheath, a cytoskeletal structure surrounding the axoneme in the principal piece of mammalian sperm tails. It plays a critical role in sperm motility and maturation. FSCB was first identified through proteomic studies targeting sperm components involved in fertilization and male infertility. The protein contains multiple phosphorylation sites and a calcium-binding domain, suggesting its involvement in calcium-dependent signaling pathways during sperm capacitation and the acrosome reaction.
FSCB antibodies are primarily used in reproductive biology research to investigate sperm function, structural integrity, and molecular mechanisms underlying infertility. These antibodies enable the detection and localization of FSCB in spermatozoa via techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. Studies have shown that abnormal expression or mutations in FSCB correlate with impaired sperm motility and structural defects, making it a potential biomarker for diagnosing certain forms of male infertility.
Commercial FSCB antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as recombinant fragments or synthetic peptides corresponding to conserved regions of the protein. Their application extends to comparative studies across species, given FSCB's evolutionary conservation in mammals. Ongoing research explores FSCB's interactions with other fibrous sheath proteins (e.g., CABYR) and its role in energy regulation within sperm, highlighting its significance in both basic reproductive science and clinical diagnostics.
×