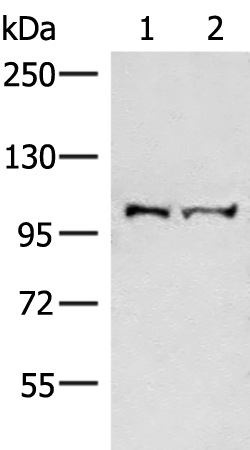
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
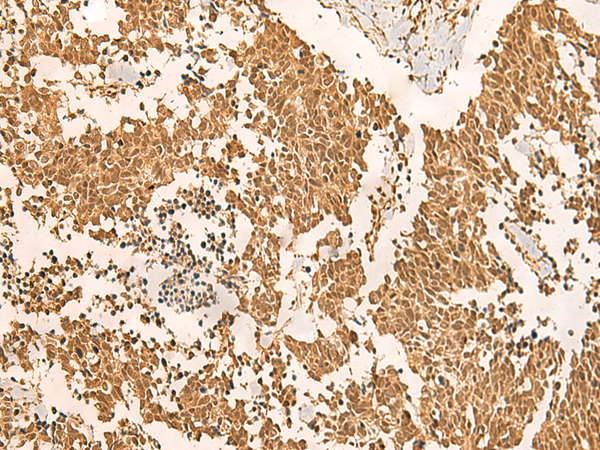
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MFDM; MFDGA; Snu114; Snrp116; SNRNP116; U5-116KD |
| WB Predicted band size | 109 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human EFTUD2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EFTUD2抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下为假设性文献,实际引用需查询真实数据库):
1. **文献名称**:*EFTUD2 Haploinsufficiency Leads to Syndromic Craniofacial Anomalies via mRNA Splicing Dysregulation*
**作者**:Lin, Y. et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,发现EFTUD2基因杂合突变导致剪接体复合物功能障碍,影响胚胎发育关键基因的mRNA剪接,与曼德布劳德-史密斯综合征(Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly, MFDM)表型相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Antibody-Based Detection of EFTUD2 in Cancer: Implications for Tumor Progression*
**作者**:Wang, H. et al.
**摘要**:利用EFTUD2特异性抗体进行免疫组化(IHC)分析,揭示其在结直肠癌中高表达,并通过调控TGF-β信号通路促进肿瘤转移,提示EFTUD2可作为潜在治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*Functional Characterization of EFTUD2 Antibodies in Zebrafish Models*
**作者**:González, F. et al.
**摘要**:通过斑马鱼模型结合抗EFTUD2抗体显微注射,证实EFTUD2缺失导致神经嵴细胞迁移异常,阐明其在颅面发育中的保守作用及分子机制。
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“EFTUD2 antibody”或“EFTUD2 immunology”,并筛选近年相关研究。
The EFTUD2 antibody targets the EFTUD2 protein, a critical component of the major spliceosome complex responsible for pre-mRNA splicing. EFTUD2 (Elongation Factor Tu GTP-Binding Domain Containing 2), also known as Snu114. plays a role in spliceosomal activation and catalytic steps, linking RNA splicing to cellular processes like gene expression regulation, cell cycle control, and DNA damage response. Mutations in the EFTUD2 gene are associated with Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly (MFDM), a rare developmental disorder characterized by craniofacial abnormalities and neurodevelopmental defects.
EFTUD2 antibodies are widely used in research to study spliceosome dynamics, protein localization, and expression levels in various tissues or disease models. They are essential tools for techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. These antibodies are often raised in hosts like rabbits or mice, with validation including knockout cell line controls to confirm specificity.
Research applications span cancer biology (investigating splicing dysregulation in tumors), neurodevelopmental disorders, and genetic syndromes linked to spliceosomal defects. EFTUD2 antibodies also contribute to understanding how splicing errors contribute to pathogenesis, offering insights into therapeutic strategies targeting spliceosome-related pathways.
×