| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
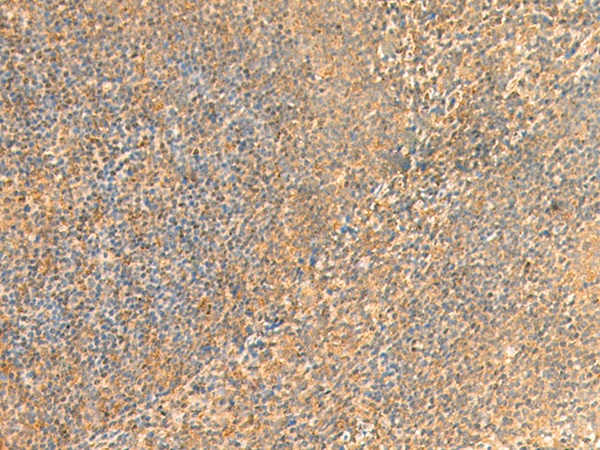
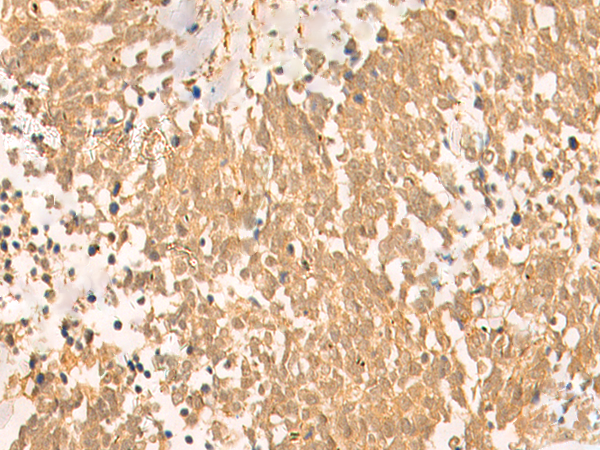
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FAT10; UBD-3; GABBR1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human UBD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于UBD抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要概述:
1. **文献名称**:*"Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for the ubiquitin-like protein FAT10/UBD"*
**作者**:Schmidtke G, et al.
**摘要**:该研究成功开发了一种针对UBD(FAT10)蛋白的高特异性单克隆抗体,验证了其在免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫荧光中的有效性,并证实UBD在炎症条件下与蛋白酶体降解途径的关联。
2. **文献名称**:*"FAT10 antibody-based analysis of protein expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues"*
**作者**:Liu Y, et al.
**摘要**:作者利用UBD(FAT10)多克隆抗体,通过免疫组织化学技术分析了肝细胞癌组织中UBD的表达水平,发现其高表达与肿瘤侵袭性和不良预后显著相关。
3. **文献名称**:*"UBD-specific antibodies reveal its role in MHC class I antigen presentation under inflammatory conditions"*
**作者**:Canaan A, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过UBD特异性抗体揭示了UBD在炎症环境下促进MHC I类分子抗原递呈的机制,并证明其通过调控蛋白酶体底物修饰影响免疫应答。
4. **文献名称**:*"A novel ELISA method for quantifying FAT10/UBD levels in human serum using paired monoclonal antibodies"*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种基于双抗夹心ELISA技术的UBD定量检测方法,开发了两种互补单克隆抗体,为UBD在自身免疫疾病中的生物标志物研究提供工具。
---
注:上述文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据具体研究补充完整信息。
UBD (Ubiquitin D), also known as FAT10 (HLA-F adjacent transcript 10), is a ubiquitin-like protein involved in post-translational modification and proteasomal degradation. Discovered in the late 1990s, UBD is encoded near the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) locus on chromosome 6 in humans. It shares structural homology with ubiquitin but functions independently, forming covalent conjugates with target proteins via its C-terminal glycine residue. UBD expression is tightly regulated and primarily induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines, particularly interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), linking it to immune and inflammatory responses.
Antibodies targeting UBD have become essential tools for studying its role in cellular processes, including protein degradation, autophagy, and immune regulation. These antibodies enable detection of UBD in various experimental settings, such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Research using UBD antibodies has revealed its overexpression in certain cancers, autoimmune diseases, and during viral infections, where it may influence antigen presentation by interacting with MHC class I molecules. Additionally, UBD knockout studies suggest its involvement in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. Despite progress, the full spectrum of UBD's physiological and pathological functions remains under investigation, with antibodies continuing to play a pivotal role in elucidating its complex interactions in health and disease.
×