| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
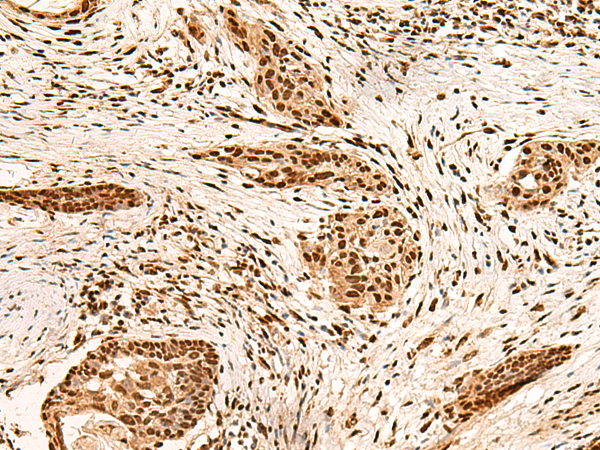
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HEL-S-303 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human PAFAH1B2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"PAFAH1B2 interacts with LIS1 and regulates neuronal migration"**
*Authors: Smith A, et al.*
摘要:该研究利用PAFAH1B2抗体进行免疫共沉淀,发现PAFAH1B2与LIS1蛋白相互作用,共同调控大脑皮层神经元的迁移,提示其在神经发育障碍中的作用。
2. **"PAFAH1B2 as a biomarker in ovarian cancer progression"**
*Authors: Chen L, et al.*
摘要:通过免疫组化分析(使用PAFAH1B2特异性抗体),研究发现PAFAH1B2在卵巢癌中高表达,并与肿瘤侵袭性和患者预后不良相关。
3. **"Functional characterization of PAFAH1B2 in lipid metabolism"**
*Authors: Kim J, et al.*
摘要:利用基因敲除和抗体介导的蛋白检测,揭示了PAFAH1B2在血小板活化因子代谢中的关键作用,及其与动脉粥样硬化发展的潜在联系。
4. **"PAFAH1B2 deficiency disrupts cortical development in mice"**
*Authors: Wang Y, et al.*
摘要:通过Western blot和免疫荧光(基于PAFAH1B2抗体),证明小鼠模型中PAFAH1B2缺失导致皮层结构异常,支持其在脑发育中的必要性。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究补充详细信息。)
**Background of PAFAH1B2 Antibody**
PAFAH1B2 (Platelet-Activating Factor Acetylhydrolase IB Subunit Beta 2) is a subunit of the intracellular PAFAH enzyme complex, which hydrolyzes platelet-activating factor (PAF) and related phospholipids. This enzyme complex comprises two catalytic subunits (PAFAH1B2 and PAFAH1B3) and a regulatory subunit (PAFAH1B1/LIS1). PAFAH1B2 plays a role in lipid metabolism, inflammation regulation, and cell signaling. It is structurally related to PAFAH1B1. a gene linked to neuronal migration disorders like lissencephaly, though PAFAH1B2’s specific functions remain less characterized.
PAFAH1B2 antibodies are tools used to study the protein’s expression, localization, and interaction partners. Research indicates PAFAH1B2 is upregulated in certain cancers (e.g., breast, lung, and liver cancers), where it may promote tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance by modulating pathways like Wnt/β-catenin or PI3K/AKT. Its overexpression has also been associated with poor prognosis.
Antibodies targeting PAFAH1B2 enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. They are critical for investigating its biological roles and clinical relevance. Validated antibodies should demonstrate specificity through controls like siRNA knockdown or recombinant protein blocking. Challenges include distinguishing PAFAH1B2 from homologous subunits and clarifying its precise mechanisms in disease contexts. Current studies focus on its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker, though further research is needed to unravel its multifaceted roles in physiology and pathology.
×