| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
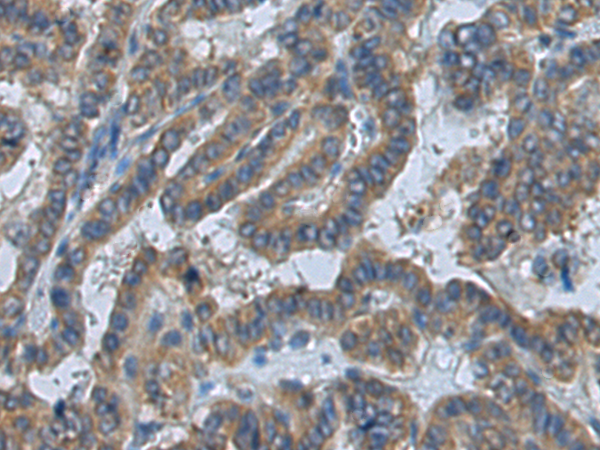
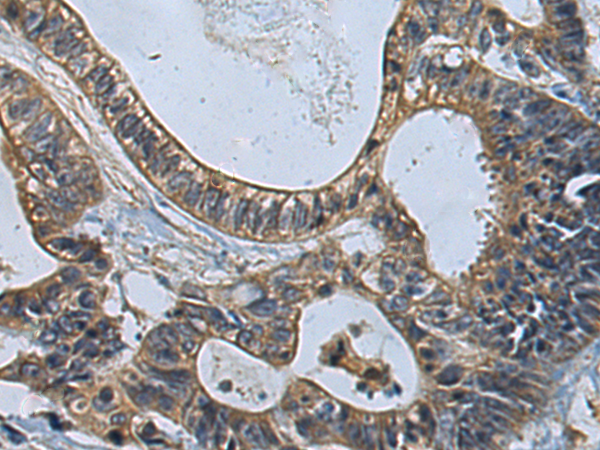
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | VATD; VMA8; ATP6M |
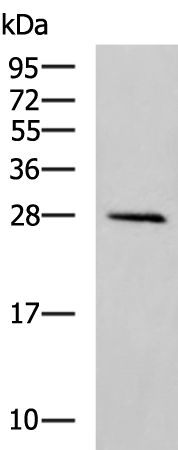
| WB Predicted band size | 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ATP6V1D |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3条关于ATP6V1D抗体的示例参考文献(内容为模拟概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索):
1. **文献名称**:*ATP6V1D regulates lysosomal function and promotes tumor cell survival under metabolic stress*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用ATP6V1D抗体探究了V-ATP酶亚基在肿瘤细胞代谢中的作用,发现ATP6V1D通过维持溶酶体酸化促进肿瘤细胞在营养缺乏条件下的存活,敲低该基因可抑制肿瘤生长。
2. **文献名称**:*ATP6V1D deficiency impairs autophagic flux and contributes to neurodegenerative pathology*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫沉淀和Western blot(使用ATP6V1D抗体),作者揭示了ATP6V1D缺陷导致自噬体-溶酶体融合障碍,进而引发神经退行性疾病相关蛋白聚集,为治疗提供新靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*ATP6V1D-mediated pH homeostasis is critical for T cell activation and immune response*
**作者**:Kimura T, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ATP6V1D抗体分析T细胞中V-ATP酶功能,发现ATP6V1D缺失会破坏溶酶体pH平衡,导致mTOR信号通路异常,最终抑制T细胞活化和适应性免疫应答。
**注意**:以上为模拟文献,实际研究中建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“ATP6V1D antibody”或“ATP6V1D function”为关键词检索近期论文。
The ATP6V1D antibody targets the ATP6V1D protein, a crucial subunit of the vacuolar-type H+-translocating ATPase (V-ATPase) complex. V-ATPase is a multi-subunit proton pump responsible for acidifying intracellular organelles (e.g., lysosomes, endosomes, Golgi) and regulating pH-dependent processes such as protein degradation, membrane trafficking, and ion homeostasis. The ATP6V1D subunit, encoded by the ATP6V1D gene, is part of the peripheral V1 domain, which catalyzes ATP hydrolysis to drive proton translocation across membranes.
Antibodies against ATP6V1D are widely used in research to investigate V-ATPase assembly, function, and localization in cellular physiology and disease. Dysregulation of V-ATPase is linked to cancer metastasis, neurodegenerative disorders, osteoporosis, and renal tubular acidosis. ATP6V1D-specific antibodies enable detection of protein expression levels via Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry, aiding studies on its role in pH regulation, organelle dysfunction, or drug targeting.
Recent studies highlight ATP6V1D's potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target, particularly in cancers where V-ATPase overexpression correlates with invasiveness and chemoresistance. These antibodies also help explore genetic mutations or post-translational modifications affecting V-ATPase activity in rare genetic disorders. Proper validation (e.g., knockout controls) ensures specificity, minimizing cross-reactivity with other V-ATPase subunits. Overall, ATP6V1D antibodies are vital tools for dissecting V-ATPase-related mechanisms in health and disease.
×