| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
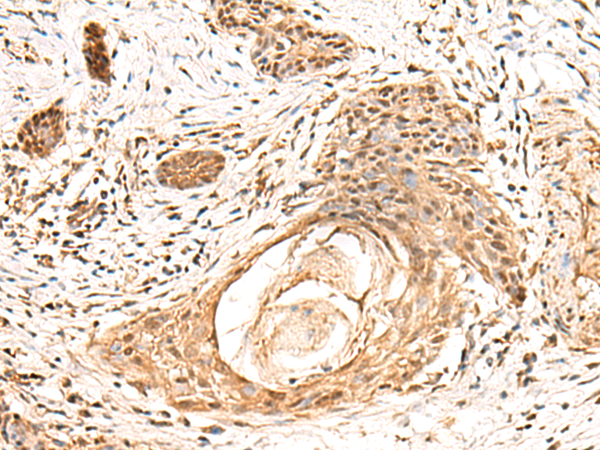
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PDIP1; FKSG86; BACURD1; POLDIP1; hBACURD1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human KCTD13 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KCTD13抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *KCTD13 is a major driver of mirrored neuroanatomical phenotypes of the 16p11.2 copy number variant*
**作者**: Golzio, C., et al. (2012)
**摘要**: 该研究通过动物模型和细胞实验,发现KCTD13作为16p11.2染色体区域的关键基因,通过调控神经细胞增殖影响脑发育。研究中使用了KCTD13抗体检测蛋白表达水平,验证其作为泛素连接酶复合体成员的功能。
2. **文献名称**: *Mutation screening of the KCTD13 gene in patients with autism spectrum disorder*
**作者**: Bacchelli, E., et al. (2013)
**摘要**: 此研究对自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)患者进行KCTD13基因突变筛查,结合Western Blot和免疫荧光技术(使用KCTD13抗体),发现特定突变导致蛋白稳定性下降,提示KCTD13异常可能与ASD发病相关。
3. **文献名称**: *Dose-dependent expression of KCTD13 regulates brain size through ubiquitination of substrate adaptors*
**作者**: McCarthy, S.E., et al. (2014)
**摘要**: 文章通过分析16p11.2拷贝数变异对脑容量的影响,揭示了KCTD13剂量敏感性的分子机制。研究利用KCTD13抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,证明其通过泛素化修饰调控下游信号通路,从而影响神经发育。
---
以上文献均涉及KCTD13抗体的实验应用,涵盖神经发育机制、疾病关联及分子功能验证等领域。如需具体文章链接或补充内容,可进一步提供信息。
The KCTD13 antibody is a research tool designed to target the KCTD13 protein, a member of the potassium channel tetramerization domain (KCTD) family. KCTD13 is encoded by the *KCTD13* gene located within the 16p11.2 chromosomal region, a locus associated with neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), intellectual disability, and obesity. The protein is implicated in ubiquitination pathways, interacting with the Cullin-3 (Cul3) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex to regulate substrate degradation, including RhoA, a key protein in cytoskeletal dynamics and neuronal migration. Dysregulation of KCTD13 has been linked to altered brain development and synaptic function.
Antibodies against KCTD13 are widely used in neuroscience and genetic research to investigate its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study KCTD13’s role in cellular processes and disease models, particularly in 16p11.2 deletion/duplication syndromes. Commercial KCTD13 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, validated for specificity in human, mouse, or rat tissues. Recent studies highlight its potential as a biomarker for neurodevelopmental disorders, driving interest in therapeutic strategies targeting KCTD13-related pathways. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibody validation and interpreting its pleiotropic roles across tissues.
×