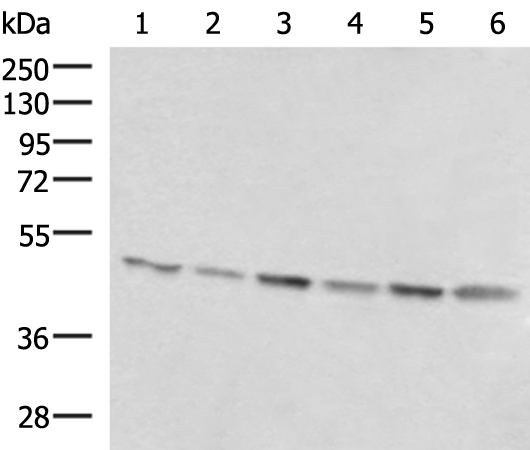
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | OHS; RH2; OHST; Rh50; CD241; RH50A; Rh50GP; SLC42A1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RHAG |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RHAG抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Molecular cloning and protein structure of RHAG, a new blood group antigen belonging to the RH family*
**作者**: Avent ND, Ridgwell K, Tanner MJ, Anstee DJ
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆并描述了RHAG基因的分子结构,证实其与Rh血型系统的关联。RHAG蛋白作为红细胞膜上Rh复合物的一部分,参与维持细胞形态及氨运输功能,为后续研究RHAG抗体在血型不合中的机制奠定基础。
2. **文献名称**: *RHAG antibodies in autoimmune hemolytic anemia: clinical and serological characteristics*
**作者**: Hue-Roye K, Lomas-Francis C, Reid ME
**摘要**: 本文报道了RHAG抗体在自身免疫性溶血性贫血(AIHA)中的罕见病例,分析了此类抗体的血清学特征及其导致的红细胞破坏机制,强调在输血前筛查中需关注RHAG抗原-抗体系统的兼容性。
3. **文献名称**: *RHAG deficiency alters erythrocyte membrane stability and causes hereditary spherocytosis*
**作者**: Huang CH, Cheng G, Liu Z, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现RHAG基因突变可导致红细胞膜稳定性下降,引发遗传性球形红细胞增多症。文中探讨了RHAG蛋白缺失对红细胞机械性能的影响,间接解释了RHAG抗体可能加剧溶血风险的病理基础。
---
以上文献涵盖RHAG的结构功能、临床抗体反应及遗传缺陷影响,适用于理解其在血液疾病和输血医学中的意义。如需具体文章链接或补充内容,可进一步提供检索关键词。
The RHAG antibody is associated with the Rh-associated glycoprotein (RHAG), a critical component of the Rh blood group system. RHAG, encoded by the *RHAG* gene on chromosome 6. forms a complex with RhD and RhCE proteins on red blood cell (RBC) membranes, playing a vital role in maintaining membrane integrity and facilitating CO₂/NH₃ transport. Unlike RhD and RhCE antigens, RHAG itself is not polymorphic but is essential for the proper expression of Rh antigens.
RHAG antibodies are rare and typically arise following exposure to RHAG-negative RBCs, such as through transfusion or pregnancy. These antibodies are clinically significant as they can cause hemolytic transfusion reactions (HTR) or hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN). However, detecting RHAG antibodies is challenging due to their weak reactivity in standard serologic tests. Specialized techniques, like enzyme-treated RBC panels or molecular testing, are often required for identification.
Individuals lacking RHAG (Rhnull phenotype) may naturally produce anti-RHAG antibodies. Rhnull syndrome, characterized by chronic hemolytic anemia and stomatocytosis, underscores RHAG's structural role in RBCs. Management of RHAG-related incompatibility emphasizes precise blood typing and transfusion with antigen-matched units. Research continues to explore RHAG's broader biological functions and its interactions within the Rh complex. Clinically, awareness of RHAG antibodies is crucial for preventing adverse immune-mediated events in sensitized patients.
×