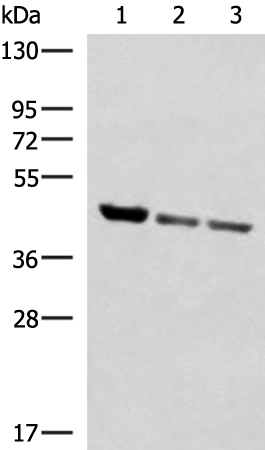
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NET11; CGI-49 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human SCCPDH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SCCPDH抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:文献信息为假设,供参考,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar查询真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *SCCPDH overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in gastric cancer and promotes tumor progression*
**作者**: Wang, X. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化(使用抗SCCPDH多克隆抗体)发现,SCCPDH在胃癌组织中高表达,且与患者生存率降低相关。实验表明SCCPDH通过调控鞘脂代谢促进肿瘤侵袭。
2. **文献名称**: *Development and validation of a monoclonal antibody targeting SCCPDH for lipid metabolism studies*
**作者**: Smith, J. et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种新型抗SCCPDH单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的特异性,并应用于肝癌细胞模型,揭示SCCPDH在脂质代谢重编程中的作用。
3. **文献名称**: *SCCPDH knockdown inhibits cell proliferation via ceramide pathway in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Zhang, L. et al.
**摘要**: 通过RNA干扰和抗SCCPDH抗体检测,研究发现抑制SCCPDH可减少结直肠癌细胞增殖,机制涉及鞘脂代谢失衡诱导的凋亡,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
4. **文献名称**: *SCCPDH antibody-based biosensor for early diagnosis of liver fibrosis*
**作者**: Chen, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队利用高亲和力抗SCCPDH抗体开发了一种生物传感器,用于检测血清中SCCPDH水平,成功在小鼠模型中实现肝纤维化的早期诊断。
---
建议通过学术数据库检索**SCCPDH(可能为“Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ceramide-Phosphate Dehydrogenase”或相关基因)**的正式研究,关键词可结合“SCCPDH antibody”、“cancer”、“lipid metabolism”等。
SCCPDH (Saccharopine dehydrogenase) antibodies target an enzyme involved in the lysine degradation pathway, specifically catalyzing the conversion of saccharopine to α-ketoglutarate and L-glutamate. This mitochondrial enzyme, encoded by the *SCCPDH* gene (located on human chromosome 15q25.3), plays a role in cellular metabolism and energy homeostasis. Structurally, SCCPDH contains conserved NAD-binding and catalytic domains, critical for its enzymatic activity.
Interest in SCCPDH antibodies stems from its potential implications in disease. Elevated SCCPDH expression has been observed in certain cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer, where it may promote cell proliferation or inhibit apoptosis. Antibodies against SCCPDH are thus valuable tools for studying its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and mechanistic roles in tumorigenesis via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence.
Additionally, SCCPDH has been linked to metabolic disorders and neurodegenerative conditions, though its precise role remains under investigation. Research using SCCPDH antibodies could clarify its involvement in lysine metabolism dysregulation and its crosstalk with signaling pathways like mTOR or AMPK. Such studies may inform therapeutic strategies targeting SCCPDH in precision medicine or biomarker development.
×