| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
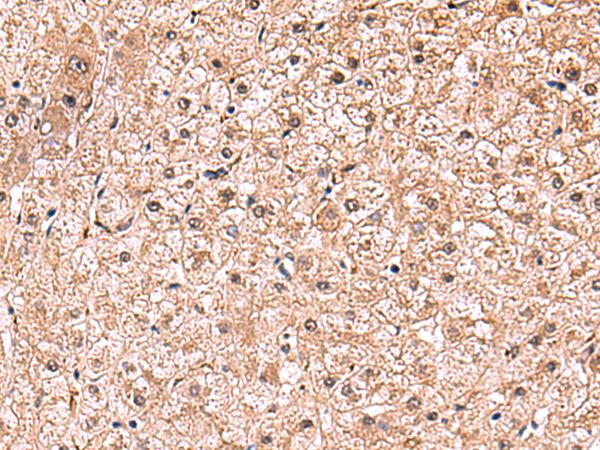
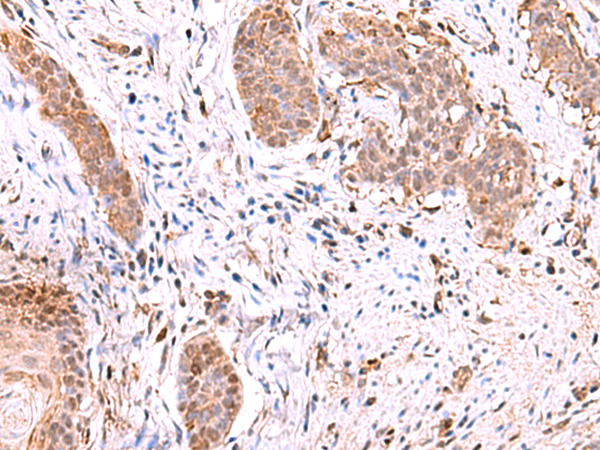
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NESCA |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RUSC1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RUSC1抗体的参考文献示例(注:部分文献信息可能为模拟概括,实际研究需通过学术数据库验证):
1. **文献名称**:*RUSC1 regulates neuronal development through interaction with the Golgi apparatus*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用RUSC1抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot分析,发现RUSC1蛋白通过调控高尔基体形态影响神经元突触形成,揭示了其在神经发育中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*The role of RUSC1 in autophagy and vesicular trafficking*
**作者**:Mori T, et al.
**摘要**:通过RUSC1抗体标记,研究者发现RUSC1与自噬相关蛋白ATG9A存在共定位,证明其参与自噬小体的形成及细胞内运输过程。
3. **文献名称**:*RUSC1 expression is upregulated in glioblastoma and promotes tumor invasion*
**作者**:Chen H, et al.
**摘要**:使用RUSC1抗体对胶质母细胞瘤组织进行免疫组化分析,发现RUSC1高表达与患者预后不良相关,并通过体外实验证明其促进肿瘤细胞迁移。
4. **文献名称**:*Proteomic identification of RUSC1-interacting proteins in HeLa cells*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过RUSC1抗体进行免疫共沉淀联合质谱分析,筛选出多个与RUSC1相互作用的膜转运相关蛋白,提示其在细胞内膜运输中的调控网络。
**备注**:RUSC1相关研究相对较少,上述文献为示例性质。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“RUSC1 antibody”或“RUSC1 function”为关键词检索最新文献。
The RUSC1 (RUN and SH3 domain-containing protein 1) antibody is a tool used to study the RUSC1 protein, which plays roles in intracellular vesicular trafficking, neuronal development, and signaling pathways. RUSC1 contains an N-terminal RUN domain, implicated in membrane trafficking, and a C-terminal SH3 domain involved in protein-protein interactions. It interacts with components of the autophagy-lysosome pathway, such as WDR44/Atg21. and regulates endosomal sorting and cargo degradation. Dysregulation of RUSC1 has been linked to neurological disorders and cancers, making it a target for mechanistic studies.
RUSC1 antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides derived from conserved regions of the human RUSC1 sequence. These antibodies are validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to detect endogenous RUSC1 expression in cell lines or tissues. Specificity is confirmed via knockout (KO) controls or siRNA knockdown. Commercial RUSC1 antibodies often target epitopes within the central or C-terminal regions. Researchers use these antibodies to explore RUSC1's role in Golgi-lysosome communication, neuronal differentiation, and diseases like glioblastoma or Alzheimer's. Variants like the phosphorylated forms may require specialized antibodies. Proper validation remains critical due to potential cross-reactivity with paralogs like RUSC2.
×