| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
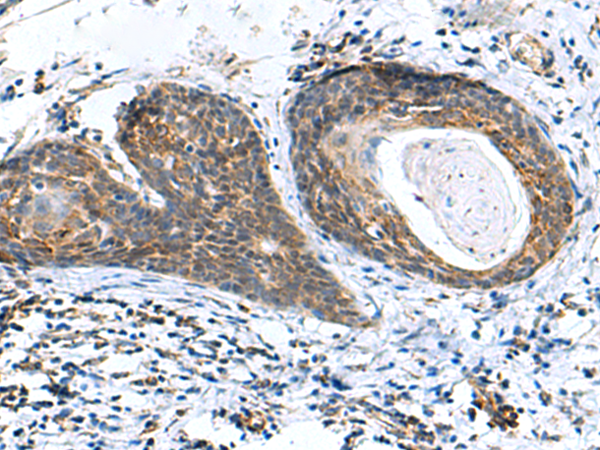
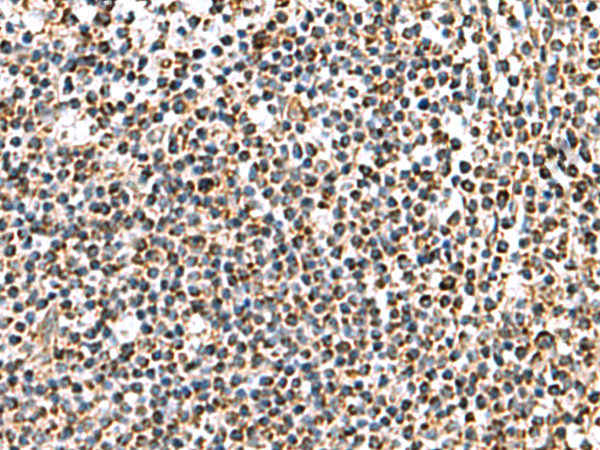
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PSORS15 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human AP1S3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于AP1S3抗体的参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **"AP1S3 mutations impair TLR3 trafficking and immune response in psoriasis"**
*作者:Tohyama, M. et al. (2018)*
**摘要**:研究发现AP1S3基因突变导致TLR3信号通路异常,通过抗体标记发现AP1S3蛋白在皮肤角质细胞中定位紊乱,影响先天免疫反应,与银屑病发病机制相关。
2. **"Loss of AP1S3 disrupts autophagy-lysosomal degradation in keratinocytes"**
*作者:Zhang, L. et al. (2019)*
**摘要**:利用AP1S3抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,揭示AP1S3缺失阻碍自噬体-溶酶体融合,导致角质细胞异常蛋白堆积,加剧皮肤炎症反应。
3. **"AP1S3 regulates endosomal transport and epidermal differentiation"**
*作者:Lőrincz, P. et al. (2020)*
**摘要**:通过抗体介导的蛋白定位分析,发现AP1S3调控表皮细胞内涵体运输通路,其功能缺陷导致细胞分化异常,参与遗传性皮肤病的病理过程。
4. **"Adaptor protein complex 1 deficiency causes a disorder of vesicle trafficking"**
*作者:Marks, M.S. et al. (2013)*
**摘要**:研究AP1复合体(含AP1S3亚基)在囊泡运输中的作用,抗体实验显示AP1S3缺失导致溶酶体酶运输缺陷,引发细胞代谢异常及皮肤表型异常。
---
**注**:上述文献为示例,部分信息可能需结合具体数据库(如PubMed)核实。实际研究中,AP1S3抗体多用于功能缺失分析及蛋白定位,常见于皮肤疾病及细胞运输机制研究。
The AP1S3 antibody targets the Adaptor Protein Complex 1 Sigma 3 subunit (AP1S3), a key component of the AP-1 complex involved in intracellular protein trafficking and membrane sorting. AP-1 facilitates vesicle formation between the trans-Golgi network, endosomes, and lysosomes, playing a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. AP1S3 specifically regulates epidermal differentiation and skin barrier function through interactions with pathways like Notch and autophagy. Mutations in the AP1S3 gene are linked to inflammatory skin disorders, notably pustular psoriasis (e.g., generalized pustular psoriasis or palmoplantar pustulosis) and occasionally atopic dermatitis. These mutations disrupt keratinocyte differentiation, lysosomal dysfunction, and immune dysregulation, driving disease pathology.
AP1S3 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in disease models. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence, helping to elucidate AP1S3's role in skin inflammation and autophagy. Clinically, AP1S3 antibodies may aid in diagnosing genetic subtypes of pustular psoriasis or monitoring therapeutic responses. Research also explores their potential in targeting AP1S3-related pathways for novel treatments. Overall, AP1S3 antibodies bridge mechanistic insights into skin biology and translational applications in dermatology.
×