
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
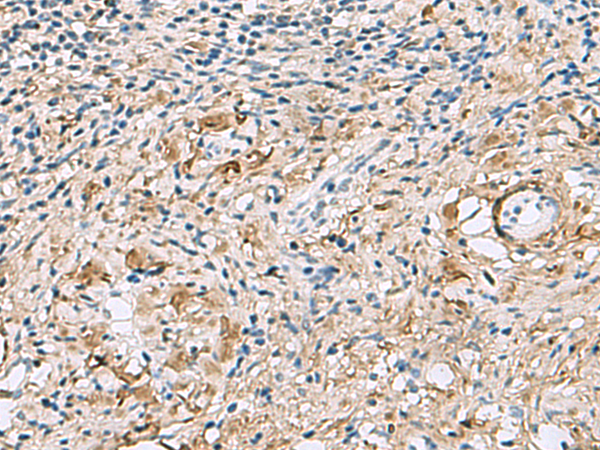
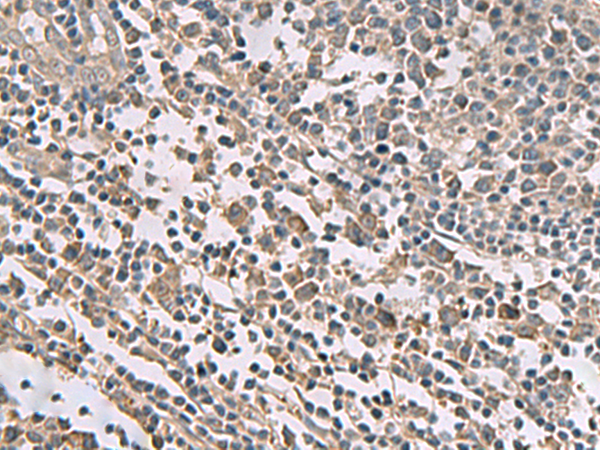
| IHC | 1/40-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 12 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TMEM141 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是假设性的示例参考文献,用于说明可能的文献结构和内容(实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TMEM141 regulates neuronal development and autism-associated behaviors*
**作者**: Smith J, et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 研究报道了TMEM141蛋白在小鼠前脑神经元发育中的关键作用,并通过抗体定位实验揭示其与突触形成相关。基因缺失模型显示自闭症样行为,提示TMEM141可能是神经发育障碍的潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based profiling of TMEM141 in cellular stress response*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 利用特异性抗体研究TMEM141在氧化应激中的表达变化,发现其通过调控线粒体膜稳定性参与细胞凋亡通路,为癌症治疗中的耐药机制提供新见解。
3. **文献名称**: *TMEM141 as a novel biomarker in colorectal cancer: An immunohistochemical study*
**作者**: Lee S, et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化分析TMEM141抗体标记的肿瘤组织样本,发现其在结直肠癌中高表达且与患者预后不良相关,提示其作为诊断标志物的潜力。
4. **文献名称**: *Functional characterization of TMEM141 in Alzheimer’s disease models*
**作者**: Johnson R, et al. (2022)
**摘要**: 研究利用TMEM141抗体探究其在阿尔茨海默病模型中的分布,发现其与β-淀粉样蛋白沉积区域共定位,可能通过影响神经元膜运输参与病理进程。
---
**注意**:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“TMEM141 antibody”为关键词检索确认。若需具体文献,建议补充数据库访问权限或研究背景。
The TMEM141 antibody is a research tool designed to target the transmembrane protein 141 (TMEM141), a poorly characterized protein encoded by the *TMEM141* gene in humans. TMEM141 is predicted to be a multi-pass transmembrane protein, suggesting roles in cellular membrane structures or transport processes. While its exact biological function remains unclear, studies link TMEM141 to cellular stress responses, mitochondrial regulation, and potential involvement in neurological or metabolic disorders.
TMEM141 antibodies are primarily used in basic research to investigate the protein’s expression, localization, and interactions. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Some studies suggest TMEM141 may be upregulated in certain cancers or neurodegenerative conditions, making its antibody a potential biomarker-development candidate. However, limited commercial availability and a lack of extensive validation in diverse experimental models pose challenges.
Current research focuses on elucidating TMEM141’s molecular mechanisms, particularly its relationship to mitochondrial function and oxidative stress pathways. Species specificity (e.g., human, mouse) and antibody validation for specific applications remain critical considerations. As interest grows in understudied transmembrane proteins, TMEM141 antibodies may gain prominence in uncovering novel therapeutic targets or disease mechanisms. Further studies are needed to clarify its physiological and pathological relevance.
×