| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
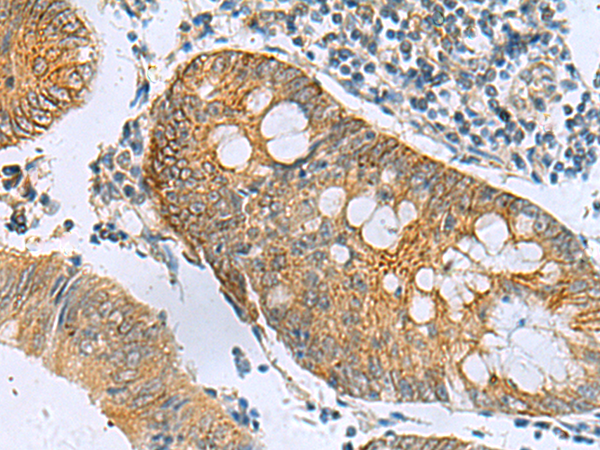
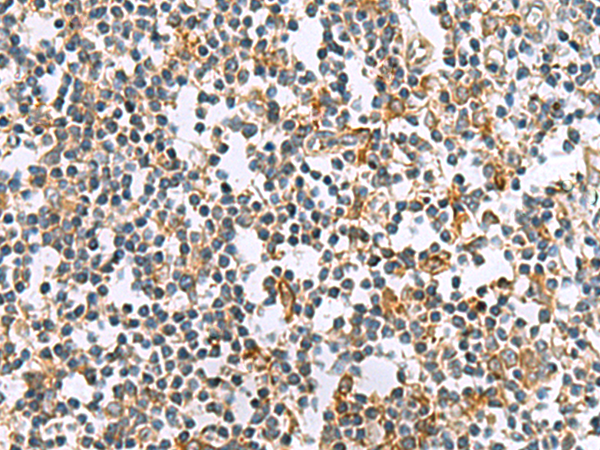
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | COD3; GCAP; GUCA; GCAP1; GUCA1; CORD14; C6orf131 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human GUCA1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GUCA1A抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容分类:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Recoverin, a novel calcium-binding protein from vertebrate photoreceptors"*
**作者**:Dizhoor, A.M., Ray, S., Kumar, S., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了GUCA1A(原名Recoverin)的钙离子结合特性,并开发了特异性抗体,用于验证其在视网膜光感受器中的表达,揭示了其通过钙依赖机制调控光信号转导的功能。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Mutations in GUCA1A cause autosomal dominant cone-rod dystrophy through structural and functional impairment of the protein"*
**作者**:Payne, A.M., Downes, S.M., Bessant, D.A., et al.
**摘要**:通过抗GUCA1A抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫组化分析,研究发现致病突变导致蛋白构象改变和稳定性下降,阐明了GUCA1A突变引发常染色体显性锥杆细胞营养不良的分子机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Calcium-sensitive conformational changes in GUCA1A and their role in modulating retinal guanylate cyclase"*
**作者**:Laura, R.P., Dizhoor, A.M., Olshevskaya, E.V.
**摘要**:利用抗GUCA1A抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示了钙离子浓度变化如何调控GUCA1A的构象,进而影响其激活视网膜鸟苷酸环化酶的能力,为光适应机制提供了关键证据。
---
这些文献涵盖了GUCA1A抗体的开发、功能验证及其在疾病机制研究中的应用,均发表于权威生物学期刊(如*Journal of Biological Chemistry*和*Human Molecular Genetics*)。如需获取全文,建议通过PubMed或ResearchGate检索标题或作者。
The GUCA1A antibody is a crucial tool in studying the GUCA1A gene product, guanylate cyclase-activating protein 1 (GCAP1), which plays a vital role in retinal phototransduction. GUCA1A encodes GCAP1. a calcium-sensing regulatory protein expressed predominantly in retinal photoreceptors. GCAP1 modulates the activity of retinal membrane guanylate cyclases (RetGCs), enzymes responsible for synthesizing cyclic GMP (cGMP), a key secondary messenger in visual signaling. Under low calcium conditions (dark adaptation), GCAP1 activates RetGCs to replenish cGMP levels, enabling photoreceptor response to light. Mutations in GUCA1A are linked to inherited retinal disorders, including autosomal dominant cone dystrophy (adCD) and cone-rod dystrophy, making the antibody valuable for investigating disease mechanisms.
The GUCA1A antibody is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect GCAP1 expression, localization, and abundance in retinal tissues or cell models. Researchers employ it to study how pathogenic mutations disrupt calcium-dependent regulation of RetGCs, leading to impaired photoreceptor function and degeneration. Its specificity ensures accurate identification of GCAP1 isoforms and post-translational modifications. Additionally, the antibody aids in evaluating therapeutic strategies targeting GUCA1A-related pathways. Commercial variants are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with validation in human and model organisms (e.g., mice, bovine), though species reactivity should be confirmed experimentally. Proper controls are essential to distinguish GCAP1 from homologous proteins like GCAP2.
×