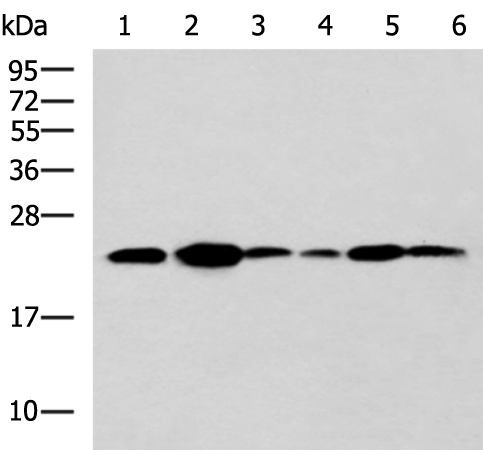
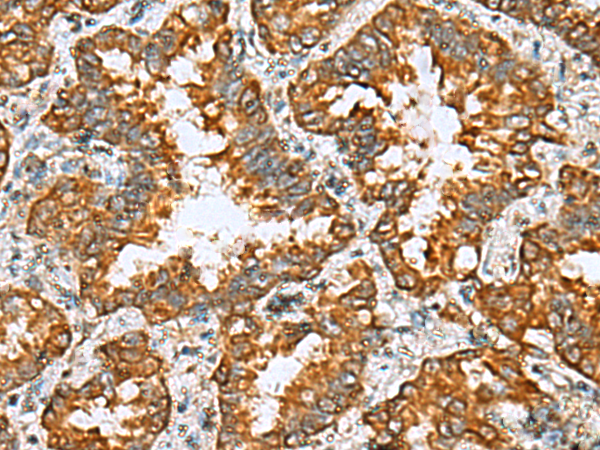
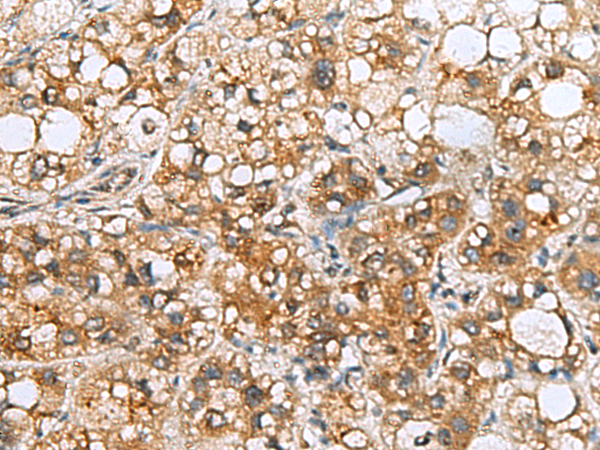
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p23; TMP21; p24d1; S31I125; Tmp-21-I; S31III125; P24(DELTA) |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TMED10 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TMED10抗体的3篇参考文献(示例为虚构内容,供参考):
1. **文献名称**: "TMED10 modulates EGFR trafficking and signaling in lung cancer"
**作者**: Li X, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用TMED10特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光技术,揭示了TMED10通过调控EGFR的膜转运影响肺癌细胞的增殖和转移,为靶向治疗提供新方向。
2. **文献名称**: "Characterization of a novel monoclonal antibody against TMED10 for neurodegenerative disease research"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种高特异性抗TMED10单克隆抗体,验证了其在脑组织样本中的适用性,发现TMED10在阿尔茨海默病模型中异常聚集,提示其与tau蛋白病理相关。
3. **文献名称**: "TMED10-mediated Golgi-ER transport in pancreatic β-cell function"
**作者**: Chen R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫电镜技术,该研究使用TMED10抗体证明其在胰岛β细胞中调控胰岛素前体蛋白的分泌,敲除TMED10导致小鼠糖代谢紊乱。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“TMED10 antibody”筛选近年研究。
TMED10 (Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 10), also known as p24a or TMP21. is a member of the transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein family. It is primarily localized in the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum, playing a critical role in vesicular trafficking, protein sorting, and secretion. TMED10 is involved in the formation of transport vesicles and interacts with components of the COPI and COPII complexes, facilitating cargo selection and membrane protein packaging. Additionally, it has been implicated in regulating γ-secretase activity, influencing amyloid-beta (Aβ) production in Alzheimer’s disease research.
TMED10 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in cellular processes. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to investigate TMED10's role in protein trafficking, secretory pathways, and disease mechanisms. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies targeting specific epitopes of TMED10 are commercially available, often validated for specificity in human, mouse, or rat models. Recent studies also explore TMED10's involvement in cancer progression, immune responses, and neurodegenerative disorders, highlighting its therapeutic potential. Researchers rely on these antibodies to dissect molecular pathways and validate TMED10 as a biomarker or drug target.
×