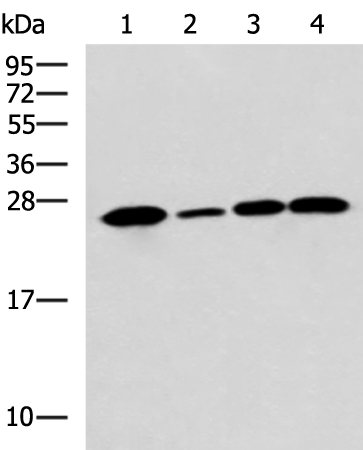
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
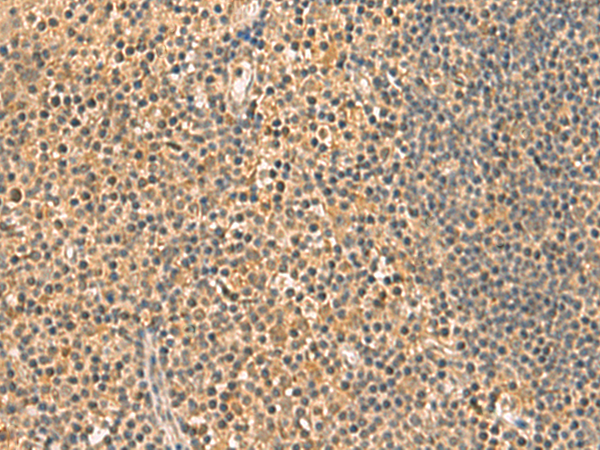
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NDGOA; PARK5; PGP95; SPG79; PGP9.5; Uch-L1; HEL-117; PGP 9.5; HEL-S-53 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human UCHL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于UCHL1抗体的3篇文献摘要简述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1) in Parkinson’s disease*
**作者**:Liu Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用UCHL1抗体检测帕金森病患者脑组织中的蛋白表达水平,发现UCHL1在病变神经元中显著减少,提示其功能缺失可能通过异常泛素-蛋白酶体途径加剧α-突触核蛋白聚集,推动疾病进展。
2. **文献名称**:*UCHL1 as a biomarker for neuroendocrine tumors*
**作者**:Thompson R.J. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析,作者使用UCHL1抗体验证其在神经内分泌肿瘤中的特异性表达,表明UCHL1可作为区分神经母细胞瘤与其他实体瘤的潜在诊断标志物,并关联其表达与患者预后。
3. **文献名称**:*The role of UCHL1 in axonal degeneration and regeneration*
**作者**:Chen Z. et al.
**摘要**:研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,结合UCHL1抗体,发现小鼠轴突损伤模型中UCHL1上调可促进神经再生,机制涉及调控泛素化平衡和减少氧化应激损伤。
---
以上文献聚焦UCHL1在疾病机制、诊断及再生中的功能,均通过UCHL1抗体进行蛋白定位或定量分析。如需具体文献来源(期刊、年份),可进一步补充。
The ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1), also known as PARK5. is a deubiquitinating enzyme predominantly expressed in neurons and neuroendocrine cells. It plays a critical role in the ubiquitin-proteasome system by hydrolyzing polyubiquitin chains to recycle ubiquitin monomers, thereby regulating protein turnover and maintaining cellular homeostasis. UCHL1 is implicated in synaptic function, axonal transport, and neurodegenerative processes. Mutations in the UCHL1 gene (e.g., S18Y polymorphism) have been linked to Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurological disorders, though its exact mechanisms remain under investigation.
UCHL1 antibodies are widely used as neuronal markers in research and diagnostics. They help identify neuronal differentiation in tissues, detect neurodegenerative changes, and study neuroendocrine tumors (e.g., neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma). In cancer biology, UCHL1 expression is associated with tumor progression and metastasis in certain malignancies. Commercially available antibodies target specific epitopes (e.g., C-terminal regions) and are validated for techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blot (WB), and immunofluorescence (IF). Researchers often prioritize clones with high specificity (e.g., EPR18729) and validate results using knockout controls or neuronal cell lines. Despite its neuronal prominence, UCHL1’s paradoxical roles—neuroprotective in some contexts yet oncogenic in others—underscore the importance of context-dependent interpretation in experimental studies.
×