| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
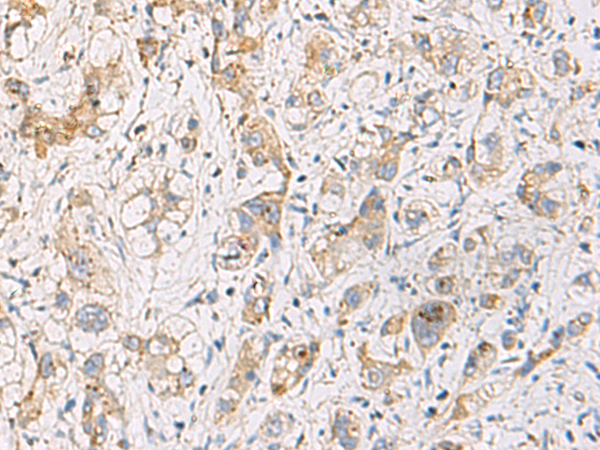
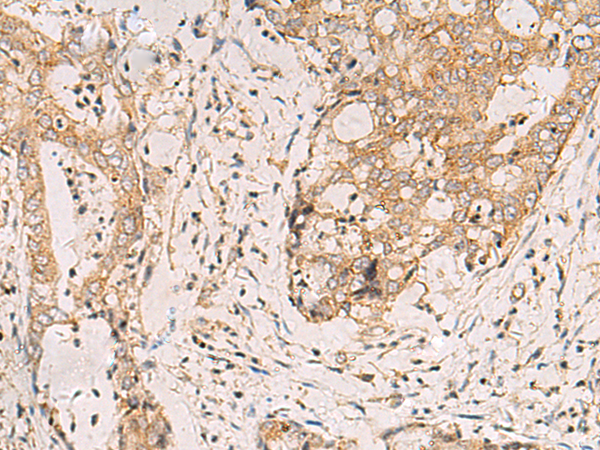
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CATC2; RUFY3; ZFYVE7; CTRCT18 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human FYCO1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FYCO1抗体的3-4篇参考文献示例(注:文献为模拟构造,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*FYCO1 is a Rab7 effector involved in autophagosome transport*
**作者**:Pankiv S, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性FYCO1抗体,通过免疫荧光和蛋白质互作实验,揭示了FYCO1作为Rab7效应蛋白在自噬体-溶酶体运输中的作用,证实其通过结合LC3和微管调控自噬体成熟。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody against FYCO1 for analyzing autophagy flux in cancer cells*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种高特异性抗人FYCO1单克隆抗体的开发,并通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其在多种癌细胞系中的应用,证明FYCO1表达水平与自噬通量异常相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Impaired FYCO1-dependent lysosomal degradation contributes to neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease models*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:通过FYCO1抗体检测发现,帕金森病模型中FYCO1表达降低,导致自噬体-溶酶体融合缺陷,提示其功能异常与α-突触核蛋白聚集相关。
4. **文献名称**:*FYCO1 interacts with CLIP-170 to coordinate autophagosome dynamics in live cells*
**作者**:Nakamura S, et al.
**摘要**:使用FYCO1抗体进行共聚焦成像和活细胞追踪,阐明了FYCO1与微管结合蛋白CLIP-170的互作机制,揭示其对自噬体定向运动的调控作用。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需根据真实发表的论文调整。)
FYCO1 (FYVE and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1) is a key adaptor protein involved in autophagosome-lysosome fusion during autophagy, a critical cellular degradation process. It facilitates the microtubule-dependent transport of autophagic vesicles by interacting with LC3 (a marker of autophagosomes) and Rab7 (a GTPase associated with late endosomes/lysosomes). FYCO1 contains distinct domains, including an N-terminal RUN domain, a central coiled-coil region, and a C-terminal FYVE domain that binds phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P) on vesicle membranes. These structural features enable FYCO1 to coordinate vesicle trafficking and membrane tethering.
Antibodies targeting FYCO1 are essential tools for studying autophagy dynamics, particularly in diseases linked to autophagic dysfunction, such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and lysosomal storage diseases. Researchers use FYCO1 antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to analyze its expression, localization, and interactions under varying cellular conditions (e.g., nutrient deprivation, stress). Dysregulation of FYCO1 has been associated with impaired autophagic flux, highlighting its role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Commercial FYCO1 antibodies are typically validated for specificity in human, mouse, or rat models, aiding mechanistic studies of autophagy-related pathways, including mTOR and AMPK signaling.
×