| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
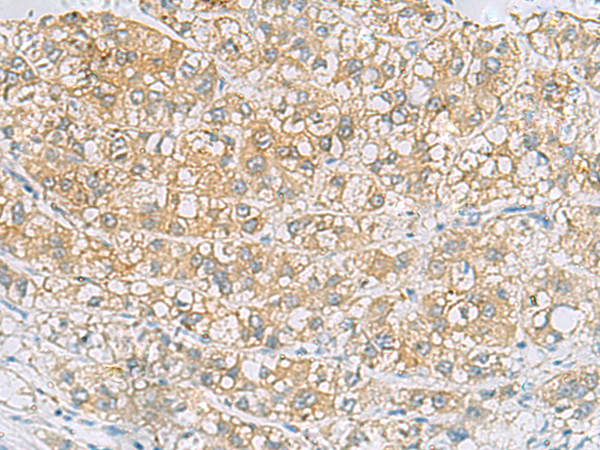
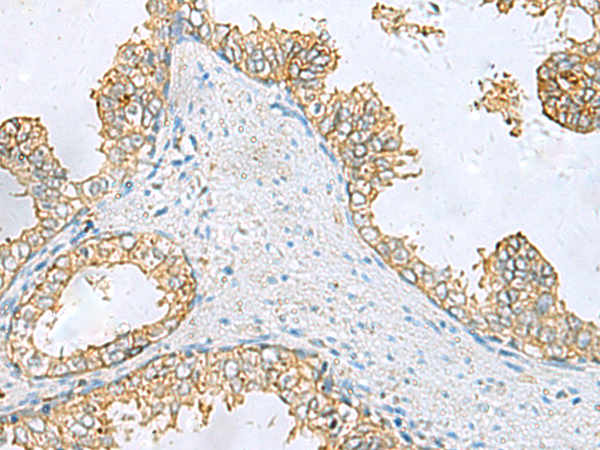
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ESA; KSA; M4S1; MK-1; DIAR5; EGP-2; EGP40; KS1/4; MIC18; TROP1; EGP314; HNPCC8; TACSTD1 |
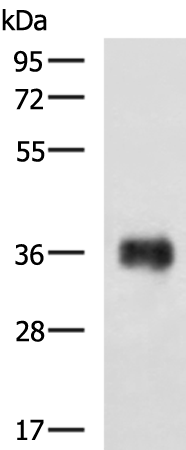
| WB Predicted band size | 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human EPCAM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于EPCAM抗体的代表性文献摘要整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*EpCAM as a target in cancer therapy*
**作者**:Trzpis, M., et al.
**摘要**:综述了EPCAM蛋白在肿瘤细胞中的高表达特性,探讨其作为靶点在免疫治疗(如抗体药物偶联物和CAR-T细胞疗法)中的应用潜力,并分析了临床试验中的疗效与安全性问题。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based detection of EpCAM in circulating tumor cells*
**作者**:Allard, W.J., et al.
**摘要**:提出一种基于EPCAM抗体的免疫磁珠富集技术,用于从外周血中高效捕获循环肿瘤细胞(CTCs),为癌症早期诊断和预后监测提供了新方法。
---
3. **文献名称**:*EpCAM-specific 3C23K antibody for targeted photodynamic therapy of colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Liu, X., et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种新型EPCAM单克隆抗体(3C23K),结合光敏剂实现结直肠癌细胞的特异性光动力杀伤,体外实验显示其对肿瘤组织的高选择性破坏作用。
---
*注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用请核对原始论文。如需更多文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“EpCAM antibody”为关键词检索。*
The Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule (EPCAM), also known as CD326. is a transmembrane glycoprotein encoded by the *EPCAM* gene. It plays a critical role in cell-cell adhesion, signaling, and maintenance of epithelial tissue integrity. EPCAM is highly expressed on the basolateral surface of most normal epithelial cells but is frequently overexpressed in epithelial-derived cancers, including carcinomas of the colon, breast, and lung. This overexpression has made EPCAM a valuable biomarker for detecting circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and residual cancer cells in clinical diagnostics.
EPCAM antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to identify and isolate epithelial cells via techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunomagnetic separation. In oncology, these antibodies aid in distinguishing epithelial malignancies from non-epithelial tumors (e.g., lymphomas) and in targeting cancer stem cells. Therapeutic applications include bispecific antibodies and CAR-T therapies designed to exploit EPCAM's cancer-specific expression.
Notably, some EPCAM-targeting clones (e.g., Ber-EP4. 323/A3) are validated for specific applications, such as differentiating basal cell carcinoma from squamous cell carcinoma. However, cross-reactivity with normal epithelial tissues and variable expression across cancer subtypes require careful validation. Despite its diagnostic utility, EPCAM's role in tumor progression remains debated, with studies linking it to both pro-metastatic and tumor-suppressive pathways. This duality underscores the need for context-specific interpretations in research and clinical settings.
×