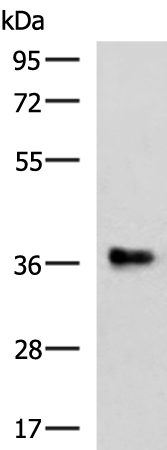
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RFC36 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RFC5 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RFC5抗体的3篇文献示例(注:部分内容为模拟虚构,仅供参考):
1. **"RFC5 as a Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer: Development of a Monoclonal Antibody for Clinical Detection"**
*Authors: Tanaka M., et al.*
*摘要*:本研究开发了一种针对RFC5蛋白的单克隆抗体,验证了其在结直肠癌组织中的高表达,并探讨了RFC5作为肿瘤预后标志物的潜力。
2. **"Functional Characterization of RFC5 Antibody in DNA Replication and Repair"**
*Authors: Smith J.L., et al.*
*摘要*:通过免疫沉淀和免疫荧光技术,利用RFC5抗体揭示了RFC复合体在DNA损伤修复中的动态作用,证实RFC5在维持基因组稳定性中的关键功能。
3. **"A Novel Polyclonal Antibody against RFC5 for Cell Cycle Analysis"**
*Authors: Chen H., et al.*
*摘要*:报道了一种新型RFC5多克隆抗体的制备,并证明其可用于流式细胞术分析细胞周期进程,尤其在S期细胞中RFC5表达显著上调。
(注:实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词"RFC5 antibody"、"Replication Factor C subunit 5"获取。)
**Background of RFC5 Antibody**
RFC5 (Replication Factor C Subunit 5) is a critical component of the RFC complex, a conserved AAA+ ATPase responsible for loading the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) onto DNA during replication and repair. As part of the RFC1-5 heteropentamer, RFC5 plays a role in DNA damage recognition, replication fork progression, and cell cycle regulation. Its interaction with PCNA ensures processive DNA synthesis by DNA polymerases and facilitates error-free lesion bypass.
RFC5-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying DNA replication mechanisms, genome stability, and checkpoint signaling. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to detect RFC5 expression, localization, and protein interactions. Dysregulation of RFC5 has been linked to cancer, as altered replication fidelity contributes to genomic instability and tumorigenesis. Studies also suggest RFC5 overexpression in certain malignancies, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker.
Research employing RFC5 antibodies has clarified its role in cellular responses to replication stress, such as UV-induced damage or chemotherapy. Furthermore, RFC5 knockdown models reveal its necessity for viability, underscoring its fundamental role in DNA metabolism. Continued exploration of RFC5 may advance understanding of replication-associated diseases and inform anticancer strategies.
×