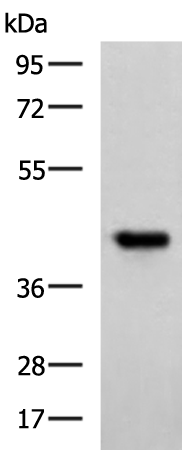
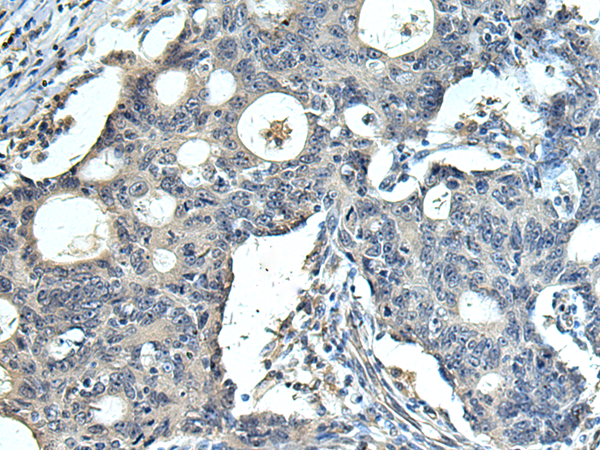
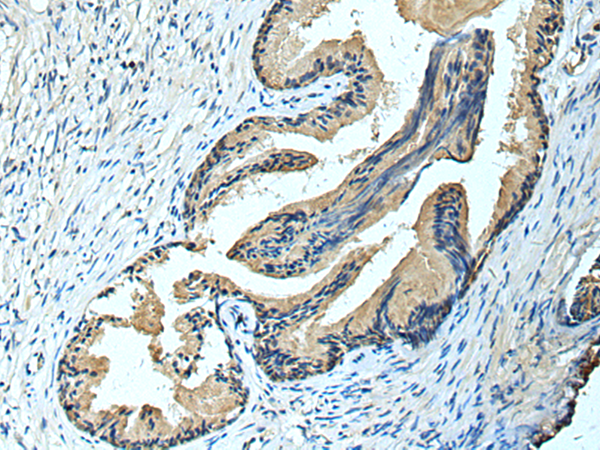
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FCRL; FCRX; FREB; FCRL1; FCRLX; FCRLb; FCRLd; FCRLe; FCRLM1; FCRLc1; FCRLc2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human FCRLA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"FCRLA, a novel Fc receptor-like molecule expressed in B cells"** by Davis et al. (2002)
摘要:首次克隆并描述了FCRLA的分子特征,揭示其在B细胞中的特异性表达,并推测其可能参与B细胞受体信号调控。
2. **"FCRLA is a resident endoplasmic reticulum protein in human B cells"** by Wilson et al. (2010)
摘要:研究通过免疫荧光和亚细胞定位分析,证实FCRLA定位于内质网,可能在未成熟B细胞中调节免疫球蛋白组装或质量控制。
3. **"FCRLA expression in autoimmune diseases and its interaction with immunoglobulins"** by Li et al. (2016)
摘要:探讨FCRLA在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)等自身免疫疾病患者B细胞中的异常表达,提示其可能与自身抗体产生相关。
4. **"FCRLA as a biomarker for germinal center-derived B-cell lymphomas"** by Schneider et al. (2018)
摘要:分析FCRLA在滤泡性淋巴瘤中的高表达,提出其作为生发中心来源B细胞肿瘤的潜在诊断标志物。
(注:以上文献信息为示例概括,实际引用需核对具体论文内容及发表细节。)
Fc receptor-like A (FCRLA) is an intracellular protein predominantly expressed in B lymphocytes and germinal center-associated cells. Unlike classical Fc receptors, FCRLA lacks a transmembrane domain and does not directly bind immunoglobulins. Discovered in the early 2000s, it belongs to the Fc receptor homolog (FCRH) family, encoded within the human leukocyte receptor complex. FCRLA is thought to play a regulatory role in B cell development and antibody production, potentially interacting with immunoglobulins during their assembly in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Antibodies targeting FCRLA are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Research using FCRLA antibodies has linked the protein to autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus), B cell malignancies, and immunodeficiency disorders, suggesting its involvement in immune regulation. However, the exact molecular mechanisms of FCRLA remain unclear, partly due to its unique intracellular retention and lack of direct ligand-binding activity.
FCRLA antibodies are particularly valuable in exploring its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target in B cell-related pathologies. Their development has advanced understanding of FCRLA's role in balancing immune activation and tolerance, though further studies are needed to clarify its precise biological functions.
×