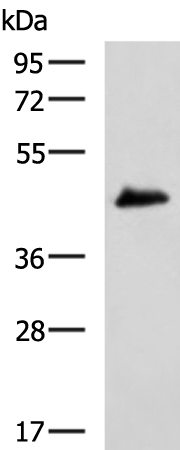
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
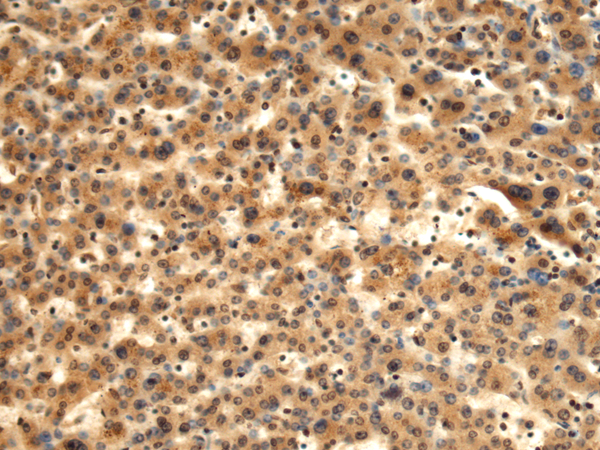
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TMOD; ETMOD; D9S57E |
| WB Predicted band size | 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TMOD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TMOD1抗体的3篇参考文献,简要列举如下:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Tropomodulin1: A key regulator of erythrocyte membrane stability"*
**作者**:Fowler VM, Sussman MA, Miller PG
**摘要**:该研究利用TMOD1特异性抗体,通过免疫荧光和Western blot技术,揭示了TMOD1在维持红细胞膜骨架稳定性中的作用,表明其通过与肌动蛋白丝结合调节细胞形态和机械强度。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Localization of tropomodulin1 in neuronal growth cones and its role in actin filament organization"*
**作者**:Almenar-Queralt A, Lee A, Condeelis JS, et al.
**摘要**:作者通过TMOD1抗体的免疫组化分析,发现其在神经元生长锥中的分布,证明TMOD1通过调控肌动蛋白丝长度影响神经突触的可塑性和轴突导向。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Tropomodulin1 overexpression alters cardiomyocyte sarcomere structure and function"*
**作者**:Sussman MA, Welch S, Gude N, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用TMOD1抗体进行心肌细胞免疫染色,发现TMOD1过表达会破坏肌节中肌动蛋白的动态平衡,导致心脏收缩功能异常,强调了其在心肌细胞中的关键调控作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对具体信息。若需更近期研究,可检索关键词“TMOD1 antibody + 应用场景(如Western blot/IF)”。
The TMOD1 antibody is a crucial tool in studying tropomodulin 1 (TMOD1), a cytoskeletal protein that regulates actin filament dynamics by capping their pointed ends. TMOD1 plays a vital role in maintaining the stability and length of actin filaments, particularly in erythrocytes and muscle cells, where it ensures structural integrity and functional contractility. Dysregulation of TMOD1 has been linked to various pathologies, including cardiomyopathies, muscular dystrophies, and blood disorders like hemolytic anemia.
The TMOD1 antibody is widely used in immunoassays (e.g., Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence) to detect TMOD1 expression, localization, and interactions in cells and tissues. Researchers employ it to investigate TMOD1's role in cell morphology, mechanical properties, and signaling pathways. Polyclonal and monoclonal variants are available, typically generated in rabbits or mice using recombinant TMOD1 protein fragments. Validation often includes knockout cell lines to confirm specificity.
Recent studies highlight TMOD1's potential as a biomarker in cancer, where its aberrant expression correlates with tumor progression and metastasis. The antibody also aids in exploring therapeutic targets for diseases linked to actin cytoskeleton dysfunction. Its application spans cell biology, pathology, and drug development, underscoring its importance in both basic research and clinical investigations.
×