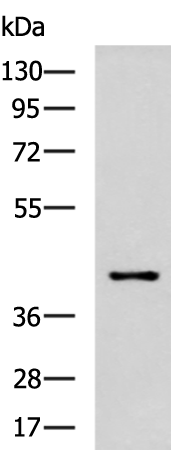
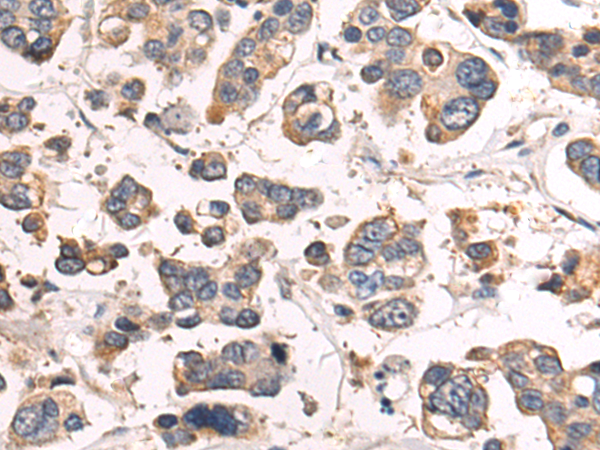
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PIX2; SOFT; WDR51A |
| WB Predicted band size | 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human POC1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于 **POC1A抗体** 的3篇参考文献,涵盖其功能、疾病关联及实验应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in POC1A Cause Syndromic Retinal Dystrophy*
**作者**:Shaheen et al. (2016)
**摘要**:首次报道人类 **POC1A** 纯合突变导致纤毛病综合征(视网膜营养不良、骨骼异常),通过外显子测鉴定了突变位点,并验证POC1A蛋白在中心体组装中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*POC1A is essential for centriole duplication and interact with CEP135*
**作者**:Venoux et al. (2013)
**摘要**:研究发现 **POC1A** 通过结合CEP135调控中心体复制,敲低POC1A导致细胞周期停滞和中心体异常,证实其在有丝分裂中的必要功能。
3. **文献名称**:*POC1A truncation mutations cause ciliopathy with obesity and insulin resistance*
**作者**:Keller et al. (2018)
**摘要**:在小鼠模型中验证 **POC1A** 截短突变引发纤毛功能障碍,导致代谢异常(肥胖、胰岛素抵抗),并证明其抗体在定位纤毛基底体的应用价值。
---
以上文献可用于研究POC1A在纤毛病、细胞周期或代谢疾病中的机制及抗体实验设计。如需具体实验细节或DOI,可进一步补充。
The POC1A (Proteasome Assembly Chaperone 1 Homolog A) antibody is a tool used to study the POC1A protein, a conserved eukaryotic protein critical for centriole duplication, ciliogenesis, and cell cycle progression. POC1A functions as a structural component of centrioles, playing a key role in maintaining centrosome integrity and ensuring proper spindle formation during mitosis. It interacts with other centriolar proteins like SAS-6 and CEP135 to stabilize centriole architecture. Dysregulation of POC1A is linked to ciliopathies, microcephaly, and cancers, as aberrant centrosome dynamics can lead to genomic instability.
Research using POC1A antibodies has elucidated its dual role in both early centriole assembly and late-stage maturation. The antibody is widely employed in techniques such as immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry to visualize POC1A localization (primarily at centrosomes and basal bodies) and quantify expression levels. Studies in model organisms, including zebrafish and mice, have revealed its necessity for embryonic development, particularly in tissues reliant on cilia function. Recent structural analyses using POC1A-specific antibodies also contributed to understanding its interaction networks in 3D centriole models. Commercially available polyclonal or monoclonal POC1A antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, validated for species cross-reactivity (human, mouse, rat), and used in both basic research and clinical investigations targeting ciliopathies or cancer biomarkers.
×