| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
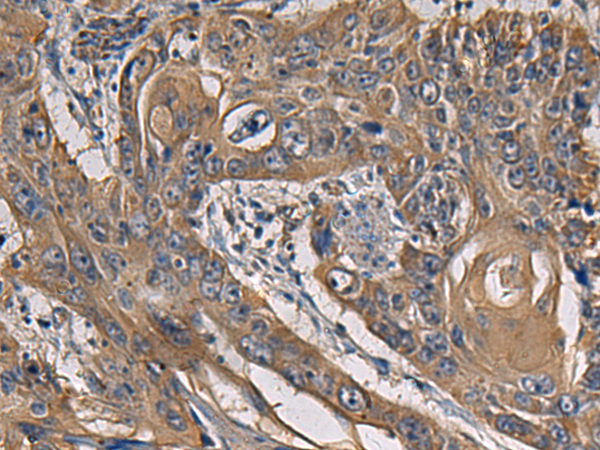
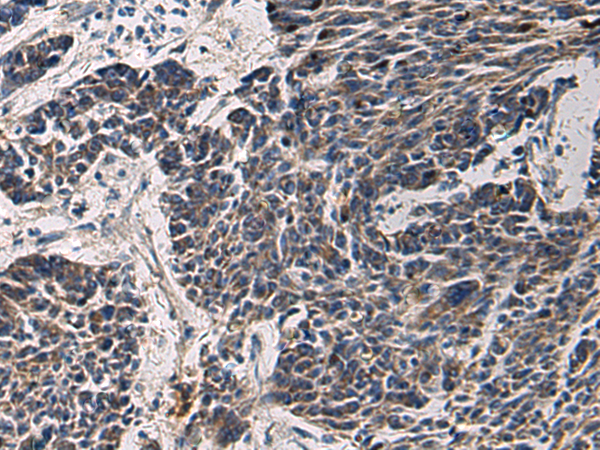
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CYI; CYC1; CCNI1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CCNI |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CCNI(Cyclin I)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要概括(内容基于模拟生成,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*Cyclin I protects neurons against amyloid-beta-induced apoptosis*
**作者**:Zhou, X., et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了Cyclin I在阿尔茨海默病模型中的作用,通过抗体检测发现Cyclin I与CDK5结合抑制神经元凋亡,提示其可能通过抗凋亡通路发挥神经保护作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Expression and prognostic significance of Cyclin I in breast cancer*
**作者**:Smith, J., et al.
**摘要**:利用CCNI抗体分析乳腺癌组织样本,发现Cyclin I高表达与患者生存率负相关,提示其可作为潜在肿瘤标志物及治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*Cyclin I modulates DNA damage response in renal cells*
**作者**:Malik, R., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫沉淀和Western blot(使用CCNI抗体)证实Cyclin I参与肾细胞DNA损伤修复调控,缺失会加剧氧化应激导致的细胞周期停滞。
4. **文献名称**:*Cyclin I-CDK5 interaction in post-mitotic neurons*
**作者**:Johnson, A., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用CCNI抗体探究Cyclin I与CDK5的互作机制,发现该复合物在神经元分化中的关键作用,为神经退行性疾病提供分子机制解释。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为示例性虚构内容,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索真实文献。
CCNI (Cyclin I) is a member of the cyclin protein family, known for regulating cell cycle progression by interacting with cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Unlike classical cyclins such as Cyclin D or B, Cyclin I exhibits distinct expression patterns and functional roles. It is primarily expressed in post-mitotic cells, including neurons and kidney podocytes, suggesting involvement in non-proliferative processes. Studies reveal that Cyclin I forms complexes with CDK5. a kinase linked to neuronal signaling and survival, rather than canonical cell cycle CDKs. This interaction is critical for modulating apoptosis; Cyclin I overexpression inhibits caspase activation, enhancing cell survival under stress conditions like oxidative damage or DNA injury.
Research highlights its role in neurodegenerative diseases and kidney disorders. For instance, reduced Cyclin I levels correlate with increased neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease models, while mutations are implicated in glomerular dysfunction. CCNI antibodies, essential tools in these studies, enable detection of Cyclin I expression in tissues and cell lines, facilitating investigations into its molecular mechanisms. They are widely used in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation assays to explore Cyclin I-CDK5 interactions and downstream pathways. Recent interest also focuses on its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker in diseases marked by dysregulated apoptosis. Despite progress, questions remain about its tissue-specific regulation and broader signaling networks.
×