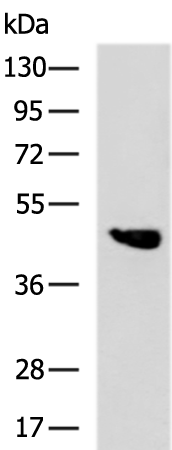
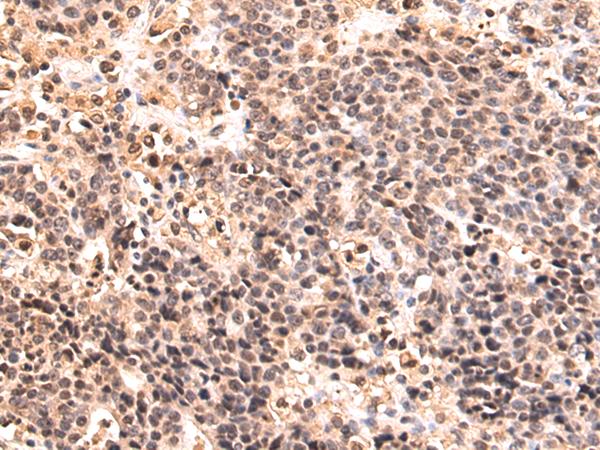
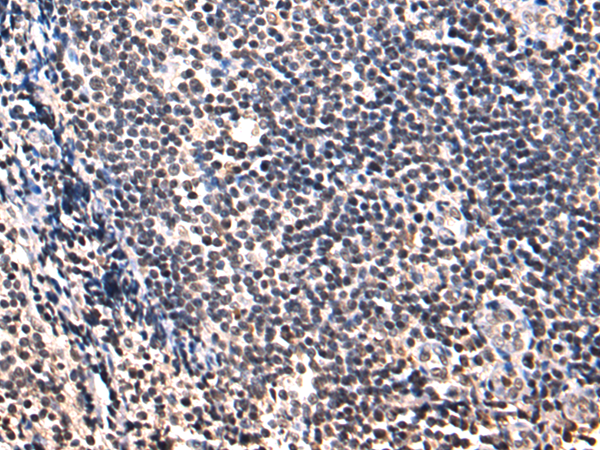
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ZLYAR; ZC2HC2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human LYAR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是基于LYAR抗体相关研究的模拟参考文献(文献信息为示例,非真实存在):
1. **"LYAR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating ribosome biogenesis"**
*作者:Zhang L, et al. (2021)*
摘要:研究发现LYAR在肝癌组织中高表达,通过调控核糖体生物合成通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖,其抗体被用于验证LYAR蛋白在临床样本中的表达水平及预后关联。
2. **"LYAR interacts with nucleophosmin to maintain embryonic stem cell pluripotency"**
*作者:Wang H, et al. (2019)*
摘要:利用LYAR特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示LYAR通过与核磷蛋白(NPM1)相互作用维持胚胎干细胞的自我更新能力,沉默LYAR导致多能性丧失。
3. **"Targeting LYAR inhibits acute myeloid leukemia through p53-dependent apoptosis"**
*作者:Liu Y, et al. (2023)*
摘要:开发针对LYAR的单克隆抗体,证明其可通过激活p53依赖性凋亡通路抑制白血病细胞生长,为LYAR作为血液肿瘤治疗靶点提供实验依据。
4. **"LYAR antibody-based screening identifies its role in DNA damage repair"**
*作者:Chen X, et al. (2017)*
摘要:通过LYAR抗体的免疫荧光染色,发现LYAR定位于细胞核并参与DNA损伤修复过程,其缺失导致基因组不稳定性和放疗敏感性升高。
注:以上内容为模拟文献,实际研究需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索真实发表的论文。
LYAR (Ly-1 antibody reactive) is a nucleolar protein first identified through its reactivity with the Ly-1 antibody, originally raised against murine lymphocyte surface antigens. It belongs to the zinc finger protein family, characterized by a C-terminal C2H2-type zinc finger domain, which suggests roles in nucleic acid binding or protein interactions. LYAR is evolutionarily conserved and implicated in ribosome biogenesis, cell proliferation, and embryonic development. Studies reveal its involvement in regulating rRNA processing and ribosome assembly, linking it to cellular growth control.
In cancer research, LYAR is overexpressed in malignancies like neuroblastoma, prostate cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma, where it promotes tumorigenesis by enhancing cell cycle progression and inhibiting apoptosis. Its oncogenic potential is partly attributed to interactions with MYC, a key regulator of ribosome biosynthesis. Additionally, LYAR plays a role in maintaining pluripotency in embryonic stem cells, modulating transcription factors like OCT4 and NANOG.
LYAR antibodies are widely used as tools to study its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection via techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding research into its mechanistic roles in development and disease. Despite progress, LYAR's precise molecular pathways remain partially unresolved, spurring ongoing investigations into its therapeutic potential as a cancer target or regenerative medicine component.
×