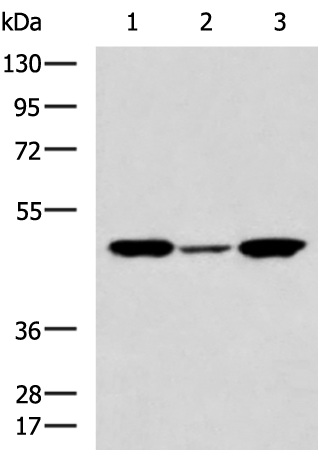
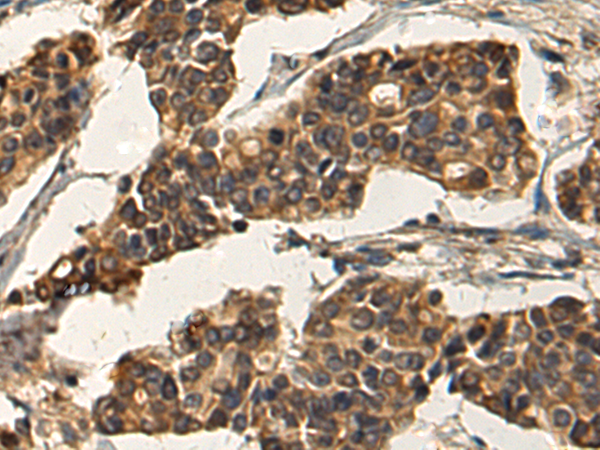
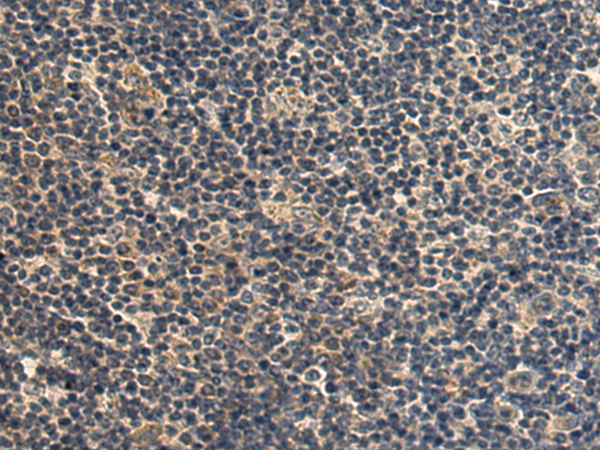
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/150-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DEP.6; DEPDC6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human DEPTOR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DEPTOR抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"DEPTOR is an mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and required for their survival"*
**作者**: Peterson, T.R. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次鉴定DEPTOR为mTOR通路的抑制蛋白,发现其在多发性骨髓瘤细胞中高表达,并通过抗体实验(Western blot、免疫沉淀)证明其通过抑制mTORC1/2活性维持肿瘤细胞存活,靶向降解DEPTOR可诱导细胞凋亡。
2. **文献名称**: *"The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling"*
**作者**: Hsu, P.P. et al.
**摘要**: 文章利用DEPTOR抗体分析mTOR复合物的调控机制,发现DEPTOR作为内源性抑制剂,通过负反馈调节mTORC1活性,影响生长因子信号传导,为代谢疾病和癌症治疗提供靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *"DEPTOR suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis via Akt-dependent pathway"*
**作者**: Zhao, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用DEPTOR抗体检测肝脏组织中蛋白表达,发现其通过Akt通路抑制糖异生和脂质合成,高表达DEPTOR可改善小鼠代谢紊乱,提示其在糖尿病和脂肪肝中的潜在作用。
4. **文献名称**: *"DEPTOR modulates cancer cell metabolism and tumor growth in a context-dependent manner"*
**作者**: Duan, S. et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化分析肿瘤样本中DEPTOR表达,发现其具有双重作用:在部分癌症中抑制mTOR通路并延缓肿瘤生长,而在特定微环境中可能通过代谢重编程促进进展,提示其功能复杂性。
---
以上研究均通过DEPTOR抗体验证蛋白表达及功能,涵盖肿瘤、代谢等领域。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar进一步检索最新进展。
DEPTOR (DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein) is a naturally occurring endogenous inhibitor of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase, a central regulator of cell growth, proliferation, and metabolism. Discovered in 2009. DEPTOR binds directly to mTOR, suppressing the activity of both mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and mTORC2. Its expression is regulated by growth factors, nutrient availability, and feedback loops within the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.
DEPTOR plays dual roles in disease contexts. While it acts as a tumor suppressor in certain cancers (e.g., multiple myeloma) by restraining mTOR-driven proliferation, elevated DEPTOR levels paradoxically promote survival in other malignancies through feedback activation of pro-growth signaling pathways. It also influences metabolic disorders, with studies linking DEPTOR dysregulation to obesity, insulin resistance, and adipose tissue dysfunction.
DEPTOR-specific antibodies are critical tools for investigating these complex biological roles. They enable detection of DEPTOR protein expression levels (often downregulated in cancers), post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation), and interactions with mTOR complexes. Commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry, these antibodies (polyclonal or monoclonal, targeting specific epitopes) help elucidate DEPTOR's tissue-specific functions and therapeutic potential. Commercial antibodies typically validate cross-reactivity with human, mouse, and rat samples. Research using DEPTOR antibodies continues to advance understanding of mTOR pathway regulation and its implications in precision oncology and metabolic disease treatment.
×