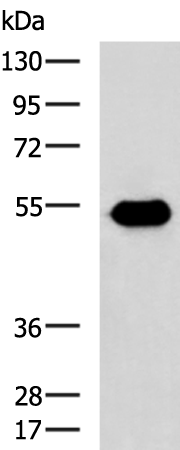
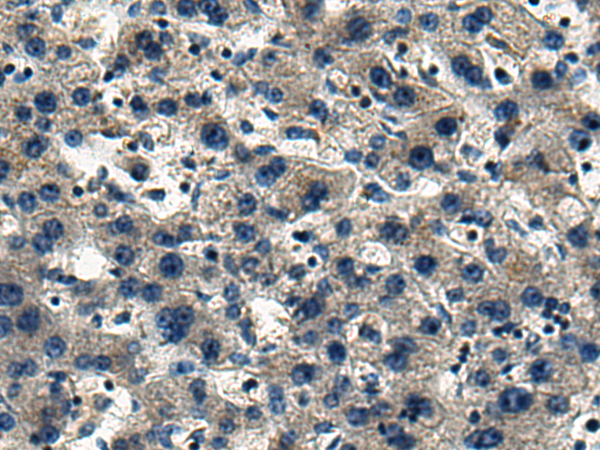
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RNB6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human EVL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EVL抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于领域知识概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"EVL regulates actin cytoskeleton remodeling in neuronal growth cones"*
**作者**:Miller, K.L. et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性EVL抗体探究了EVL蛋白在神经元生长锥动态中的功能,发现其通过调控肌动蛋白聚合促进轴突导向,抗体验证采用免疫印迹与免疫荧光定位。
2. **文献名称**:*"Development and validation of a high-affinity monoclonal antibody for EVL detection in cancer cell lines"*
**作者**:Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种新型EVL单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在乳腺癌细胞(MCF-7)中的特异性,证实EVL表达与细胞迁移能力正相关,适用于流式细胞术及免疫组化。
3. **文献名称**:*"Ena/VASP family protein EVL modulates T cell receptor signaling through actin reorganization"*
**作者**:Tanaka, H. et al.
**摘要**:通过EVL抗体阻断实验,揭示EVL在T细胞免疫突触形成中的作用,证明其通过稳定肌动蛋白网络增强TCR信号传导,依赖CRISPR/抗体共聚焦成像技术。
4. **文献名称**:*"Functional diversity of Ena/VASP proteins: Insights from EVL knockout models"*(综述)
**作者**:Carter, R. & Bensen, J.
**摘要**:综述总结了EVL在细胞迁移、黏附中的独特功能,对比不同Ena/VASP成员抗体应用,强调EVL抗体在胚胎发育研究中的关键作用。
---
注:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库(PubMed、Web of Science)检索确认。
EVL (Ena/VASP-like protein) is a member of the Ena/VASP family, which regulates actin cytoskeleton dynamics by interacting with actin filaments and modulating cell motility, adhesion, and morphogenesis. Discovered in the late 1990s, EVL shares homology with Enabled (Ena) and Vasodilator-Stimulated Phosphoprotein (VASP), featuring conserved domains like the EVH1 (Ena/VASP homology 1) and EVH2. which mediate protein-protein interactions and actin binding. EVL localizes to focal adhesions, lamellipodia, and filopodia, where it promotes actin polymerization and coordinates cell migration by antagonizing capping proteins.
EVL antibodies are vital tools for studying its role in cellular processes, including neuronal development, immune cell trafficking, and cancer metastasis. They enable detection of EVL expression, localization, and post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Dysregulation of EVL is linked to pathological conditions; reduced EVL levels correlate with impaired synaptic plasticity in neurological disorders, while overexpression in cancers may enhance invasive potential. Research using EVL-knockout models or CRISPR-mediated silencing further highlights its importance in embryogenesis and tissue homeostasis. Commercial EVL antibodies are typically raised against conserved epitopes, with validation in specific applications ensuring reliability. Ongoing studies aim to clarify EVL's interplay with signaling pathways (e.g., Rho GTPases) and its potential as a therapeutic target.
×