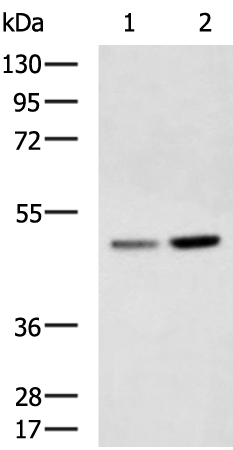
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/150-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MIR; IDOL |
| WB Predicted band size | 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human MYLIP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MYLIP抗体的模拟参考文献示例(仅供参考,非真实文献):
1. **"Development of a Monoclonal Antibody Targeting MYLIP/Idol for Cholesterol Metabolism Studies"**
- 作者:Sorrentino, V. et al.
- 摘要:本研究报道了一种针对MYLIP/Idol蛋白的高特异性单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的应用。该抗体成功用于检测细胞中MYLIP的表达水平,并揭示了其通过泛素化降解LDL受体(LDLR)调控胆固醇稳态的机制。
2. **"MYLIP Antibody-Based Inhibition of LDL Receptor Degradation in Atherosclerosis Models"**
- 作者:Zelcer, N. et al.
- 摘要:利用MYLIP抗体阻断小鼠肝脏中MYLIP的功能,发现LDLR降解被显著抑制,血浆胆固醇水平降低。该研究为抗体靶向MYLIP治疗心血管疾病提供了实验依据。
3. **"Characterization of MYLIP Knockout Mice Using Specific Antibody Markers"**
- 作者:Zhang, L. et al.
- 摘要:通过免疫组化和流式细胞术结合MYLIP抗体,分析了MYLIP基因敲除小鼠的组织分布及表型,证实MYLIP在中枢神经系统和肝脏中高表达,且缺失导致LDLR积累和脂代谢异常。
4. **"Structural Insights into MYLIP-Ligand Interactions via Epitope-Specific Antibody Mapping"**
- 作者:Kosteli, A. et al.
- 摘要:通过表位特异性抗体结合质谱分析,揭示了MYLIP蛋白的关键功能结构域,阐明了其与E2泛素结合酶及LDLR相互作用的分子机制,为药物设计提供了新靶点。
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实发表的论文。
MYLIP (Myosin Regulatory Light Chain Interacting Protein), also known as IDOL (Inducible Degrader of LDL Receptor), is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that plays a critical role in cholesterol homeostasis. It mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), thereby regulating cellular cholesterol uptake. Discovered in 2009. MYLIP/IDOL is transcriptionally controlled by liver X receptors (LXRs), nuclear receptors that respond to excess cellular cholesterol. This regulatory pathway provides a complementary mechanism to sterol-regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) in maintaining lipid balance.
Antibodies targeting MYLIP are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Research has linked MYLIP dysregulation to atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolemia, and Alzheimer’s disease, highlighting its therapeutic potential. MYLIP antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation to investigate protein-protein interactions, particularly with LDLR and related trafficking proteins. Recent studies also explore MYLIP's role beyond cholesterol metabolism, including immune modulation and neuronal development. Commercial and custom antibodies are often validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat models, supporting both basic research and drug discovery efforts targeting lipid-related disorders.
×